Page 16 - Read Online
P. 16
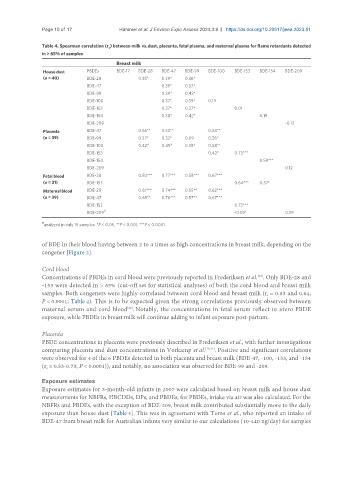
Page 10 of 17 Hammel et al. J Environ Expo Assess 2024;3:8 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jeea.2023.51
Table 4. Spearman correlation (r ) between milk vs. dust, placenta, fetal plasma, and maternal plasma for flame retardants detected
s
in > 65% of samples
Breast milk
House dust PBDEs BDE-17 BDE-28 BDE-47 BDE-99 BDE-100 BDE-153 BDE-154 BDE-209
(n = 40) BDE-28 0.35* 0.39* 0.36*
BDE-47 0.39* 0.37*
BDE-99 0.39* 0.42*
BDE-100 0.37* 0.39* 0.19
BDE-153 0.37* 0.37* 0.01
BDE-154 0.38* 0.42* 0.19
BDE-209 -0.12
Placenta BDE-47 0.56** 0.53** 0.58**
(n = 39) BDE-99 0.37* 0.32* 0.09 0.36*
BDE-100 0.42* 0.45* 0.38* 0.58**
BDE-153 0.42* 0.73***
BDE-154 0.59***
BDE-209 0.12
Fetal blood BDE-28 0.83*** 0.77*** 0.58*** 0.67***
(n = 31) BDE-153 0.64*** 0.37*
Maternal blood BDE-28 0.81*** 0.74*** 0.55** 0.62***
(n = 39) BDE-47 0.65** 0.76*** 0.57** 0.67***
BDE-153 0.73***
#
BDE-209 -0.59* 0.39
#
analyzed in only 15 samples. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001.
of BDE in their blood having between 2 to 4 times as high concentrations in breast milk, depending on the
congener [Figure 2].
Cord blood
Concentrations of PBDEs in cord blood were previously reported in Frederiksen et al. . Only BDE-28 and
[42]
-153 were detected in > 65% (cut-off set for statistical analyses) of both the cord blood and breast milk
samples. Both congeners were highly correlated between cord blood and breast milk (r = 0.83 and 0.64,
s
P < 0.0001; Table 4). This is to be expected given the strong correlations previously observed between
maternal serum and cord blood . Notably, the concentrations in fetal serum reflect in utero PBDE
[42]
exposure, while PBDEs in breast milk will continue adding to infant exposure post-partum.
Placenta
PBDE concentrations in placenta were previously described in Frederiksen et al., with further investigations
comparing placenta and dust concentrations in Vorkamp et al. [15,41] . Positive and significant correlations
were observed for 4 of the 6 PBDEs detected in both placenta and breast milk (BDE-47, -100, -153, and -154
(r = 0.53-0.73; P < 0.0001)), and notably, no association was observed for BDE-99 and -209.
s
Exposure estimates
Exposure estimates for 3-month-old infants in 2007 were calculated based on breast milk and house dust
measurements for NBFRs, HBCDDs, DPs, and PBDEs; for PBDEs, intake via air was also calculated. For the
NBFRs and PBDEs, with the exception of BDE-209, breast milk contributed substantially more to the daily
exposure than house dust [Table 5]. This was in agreement with Toms et al., who reported an intake of
BDE-47 from breast milk for Australian infants very similar to our calculations (10-440 ng/day) for samples