Page 1007 - Read Online
P. 1007
Page 8 of 11 Agbo et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:x I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.35
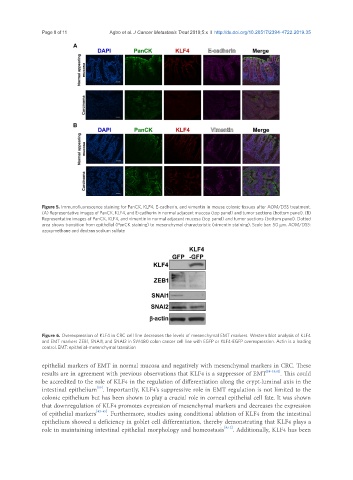
Figure 5. Immunofluorescence staining for PanCK, KLF4, E-cadherin, and vimentin in mouse colonic tissues after AOM/DSS treatment.
(A) Representative images of PanCK, KLF4, and E-cadherin in normal adjacent mucosa (top panel) and tumor sections (bottom panel). (B)
Representative images of PanCK, KLF4, and vimentin in normal adjacent mucosa (top panel) and tumor sections (bottom panel). Dotted
area shows transition from epithelial (PanCK staining) to mesenchymal characteristic (vimentin staining). Scale bar: 50 μm. AOM/DSS:
azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate
Figure 6. Overexpression of KLF4 in CRC cell line decreases the levels of mesenchymal EMT markers. Western blot analysis of KLF4
and EMT markers ZEB1, SNAI1, and SNAI2 in SW480 colon cancer cell line with EGFP or KLF4-EGFP overexpression. Actin is a loading
control. EMT: epithelial-mesenchymal transition
epithelial markers of EMT in normal mucosa and negatively with mesenchymal markers in CRC. These
results are in agreement with previous observations that KLF4 is a suppressor of EMT [28-31,41] . This could
be accredited to the role of KLF4 in the regulation of differentiation along the crypt-luminal axis in the
[10]
intestinal epithelium . Importantly, KLF4’s suppressive role in EMT regulation is not limited to the
colonic epithelium but has been shown to play a crucial role in corneal epithelial cell fate. It was shown
that downregulation of KLF4 promotes expression of mesenchymal markers and decreases the expression
of epithelial markers [42-45] . Furthermore, studies using conditional ablation of KLF4 from the intestinal
epithelium showed a deficiency in goblet cell differentiation, thereby demonstrating that KLF4 plays a
role in maintaining intestinal epithelial morphology and homeostasis [9,12] . Additionally, KLF4 has been