Page 283 - Read Online
P. 283
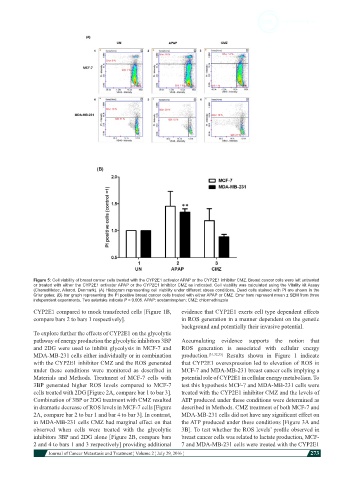
Figure 5: Cell viability of breast cancer cells treated with the CYP2E1 activator APAP or the CYP2E1 inhibitor CMZ. Breast cancer cells were left untreated
or treated with either the CYP2E1 activator APAP or the CYP2E1 inhibitor CMZ as indicated. Cell viability was calculated using the Vitality kit Assay
(ChemoMetec, Allerod, Denmark). (A) Histogram representing cell viability under different stress conditions. Dead cells stained with PI are shown in the
Q1ur gates; (B) bar graph representing the PI positive breast cancer cells treated with either APAP or CMZ. Error bars represent mean ± SEM from three
independent experiments. Two asterisks indicate P < 0.005. APAP: acetaminophen; CMZ: chlormethiazole
CYP2E1 compared to mock transfected cells [Figure 1B, evidence that CYP2E1 exerts cell type dependent effects
compare bars 2 to bars 1 respectively]. in ROS generation in a manner dependent on the genetic
background and potentially their invasive potential.
To explore further the effects of CYP2E1 on the glycolytic
pathway of energy production the glycolytic inhibitors 3BP Accumulating evidence supports the notion that
and 2DG were used to inhibit glycolysis in MCF-7 and ROS generation is associated with cellular energy
MDA-MB-231 cells either individually or in combination production. [31,32,35] Results shown in Figure 1 indicate
with the CYP2E1 inhibitor CMZ and the ROS generated that CYP2E1 overexpression led to elevation of ROS in
under these conditions were monitored as described in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells implying a
Materials and Methods. Treatment of MCF-7 cells with potential role of CYP2E1 in cellular energy metabolism. To
3BP generated higher ROS levels compared to MCF-7 test this hypothesis MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were
cells treated with 2DG [Figure 2A, compare bar 1 to bar 3]. treated with the CYP2E1 inhibitor CMZ and the levels of
Combination of 3BP or 2DG treatment with CMZ resulted ATP produced under these conditions were determined as
in dramatic decrease of ROS levels in MCF-7 cells [Figure described in Methods. CMZ treatment of both MCF-7 and
2A, compare bar 2 to bar 1 and bar 4 to bar 3]. In contrast, MDA-MB-231 cells did not have any significant effect on
in MDA-MB-231 cells CMZ had marginal effect on that the ATP produced under these conditions [Figure 3A and
observed when cells were treated with the glycolytic 3B]. To test whether the ROS levels’ profile observed in
inhibitors 3BP and 2DG alone [Figure 2B, compare bars breast cancer cells was related to lactate production, MCF-
2 and 4 to bars 1 and 3 respectively] providing additional 7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with the CYP2E1
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ July 29, 2016 ¦ 273