Page 145 - Read Online
P. 145
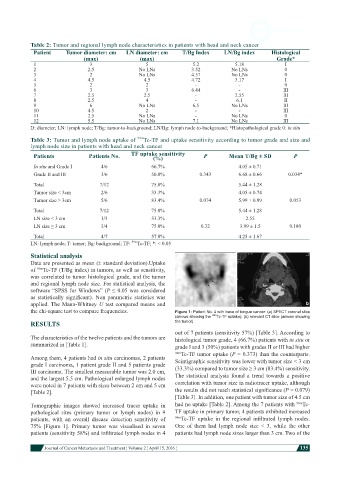
Table 2: Tumor and regional lymph node characteristics in patients with head and neck cancer
Patient Tumor diameter: cm LN diameter: cm T/Bg Index LN/Bg index Histological
(max) (max) Grade*
1 3 5 5.2 5.18 I
2 2.5 No LNs 3.52 No LNs 0
3 2 No LNs 4.57 No LNs 0
4 4.5 4.5 4.72 3.17 I
5 2 2 - - 0
6 3 3 6.44 - III
7 2.5 2.5 - 2.55 III
8 2.5 4 - 6.1 II
9 6 No LNs 6.5 No LNs III
10 4.5 2 - - III
11 2.5 No LNs - No LNs 0
12 5.5 No LNs 7.1 No LNs III
D: diameter; LN: lymph node; T/Bg: tumor-to-background; LN/Bg: lymph node-to-background; *Histopathological grade 0: in situ
Table 3: Tumor and lymph node uptake of 99m Tc-TF and uptake sensitivity according to tumor grade and size and
lymph node size in patients with head and neck cancer
Patients Patients No. TF uptake sensitivity P Mean T/Bg ± SD P
(%)
In situ and Grade I 4/6 66.7% 4.05 ± 0.71
Grade II and III 3/6 50.0% 0.343 6.68 ± 0.66 0.034*
Total 7/12 75.0% 5.44 ± 1.28
Tumor size < 3cm 2/6 33.3% 4.05 ± 0.74
Tumor size ≥ 3cm 5/6 83.4% 0.074 5.99 ± 0.99 0.053
Total 7/12 75.0% 5.44 ± 1.28
LN size < 3 cm 1/3 33.3% 2.55
LN size ≥ 3 cm 3/4 75.0% 0.32 3.99 ± 1.5 0.180
Total 4/7 57.0% 4.25 ± 1.67
LN: lymph node; T: tumor; Bg: background; TF: 99m Tc-TF; *: < 0.05
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean (± standard deviation).Uptake
of 99m Tc-TF (T/Bg index) in tumors, as well as sensitivity,
was correlated to tumor histological grade, and the tumor
and regional lymph node size. For statistical analysis, the
software “SPSS for Windows” (P ≤ 0.05 was considered
as statistically significant). Non parametric statistics was
applied. The Mann-Whitney U test compared means and
the chi-square test to compare frequencies. Figure 1: Patient No. 4 with base of tongue cancer: (a) SPECT coronal slice
(arrows showing the 99m Tc-TF uptake); (b) relevant CT slice (arrows showing
RESULTS the tumor)
out of 7 patients (sensitivity 57%) [Table 3]. According to
The characteristics of the twelve patients and the tumors are histological tumor grade, 4 (66.7%) patients with in situ or
summarized in [Table 1]. grade I and 3 (50%) patients with grades II or III had higher
99m Tc-TF tumor uptake (P = 0.373) than the counterparts.
Among them, 4 patients had in situ carcinomas, 2 patients Scintigraphic sensitivity was lower with tumor size < 3 cm
grade I carcinoma, 1 patient grade II and 5 patients grade (33.3%) compared to tumor size ≥ 3 cm (83.4%) sensitivity.
III carcinoma. The smallest measurable tumor was 2.0 cm,
and the largest 5.5 cm. Pathological enlarged lymph nodes The statistical analysis found a trend towards a positive
were noted in 7 patients with sizes between 2 cm and 5 cm correlation with tumor size in radiotracer uptake, although
[Table 2]. the results did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.079)
[Table 3]. In addition, one patient with tumor size of 4.5 cm
Tomographic images showed increased tracer uptake in had no uptake [Table 2]. Among the 7 patients with 99m Tc-
pathological sites (primary tumor or lymph nodes) in 9 TF uptake in primary tumor, 4 patients exhibited increased
patients, with an overall disease detection sensitivity of 99m Tc-TF uptake in the regional infiltrated lymph nodes.
75% [Figure 1]. Primary tumor was visualised in seven One of them had lymph node size < 3, while the other
patients (sensitivity 58%) and infiltrated lymph nodes in 4 patients had lymph node sizes larger than 3 cm. Two of the
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ April 15, 2016 ¦ 135