Page 50 - Read Online
P. 50
Page 12 of 24 Saier et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:43 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.87
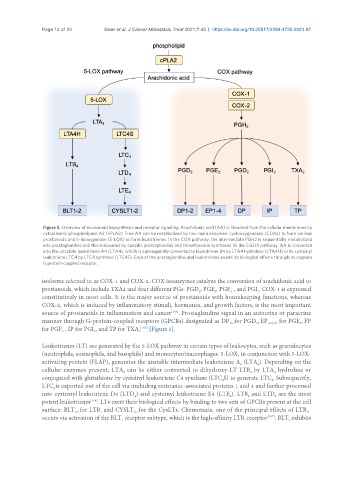
Figure 5. Overview of eicosanoid biosynthesis and receptor signaling. Arachidonic acid (AA) is liberated from the cellular membranes by
cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2). Free AA can be metabolized by two main enzymes: cyclooxygenases (COXs) to form various
prostanoids and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) to form leukotrienes. In the COX pathway, the intermediate PGH2 is sequentially metabolized
into prostaglandins and thromboxanes by specific prostaglandins and thromboxane synthases. In the 5-LOX pathway, AA is converted
into the unstable leukotriene A4 (LTA4), which is subsequently converted to leukotriene B4 by LTA4 hydrolase (LTA4H) or to cysteinyl
leukotriene LTC4 by LTC4 synthase (LTC4S). Each of the prostaglandins and leukotrienes exerts its biological effects through its cognate
G protein-coupled receptor.
isoforms referred to as COX-1 and COX-2. COX isoenzymes catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to
prostanoids, which include TXA2 and four different PGs: PGD , PGE , PGF , and PGI . COX-1 is expressed
2
2
2
2
constitutively in most cells. It is the major source of prostanoids with housekeeping functions, whereas
COX-2, which is induced by inflammatory stimuli, hormones, and growth factors, is the most important
source of prostanoids in inflammation and cancer . Prostaglandins signal in an autocrine or paracrine
[104]
manner through G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) designated as DP for PGD , EP 1/2/3/4 for PGE , FP
2
1/2
2
for PGF , IP for PGI , and TP for TXA 2 [105] [Figure 5].
2
2
Leukotrienes (LT) are generated by the 5-LOX pathway in certain types of leukocytes, such as granulocytes
(neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and monocytes/macrophages. 5-LOX, in conjunction with 5-LOX-
activating protein (FLAP), generates the unstable intermediate leukotriene A (LTA ). Depending on the
4
4
cellular enzymes present, LTA can be either converted to dihydroxy-LT LTB by LTA hydrolase or
4
4
4
conjugated with glutathione by cysteinyl leukotriene C4 synthase (LTC S) to generate LTC . Subsequently,
4
4
LTC is exported out of the cell via multidrug resistance-associated proteins 1 and 4 and further processed
4
into cysteinyl leukotriene D4 (LTD ) and cysteinyl leukotriene E4 (LTE ). LTB and LTD are the most
4
4
4
4
potent leukotrienes . LTs exert their biological effects by binding to two sets of GPCRs present at the cell
[106]
surface: BLT for LTB and CYSLT for the CysLTs. Chemotaxis, one of the principal effects of LTB ,
4
1/2
4
1/2
occurs via activation of the BLT receptor subtype, which is the high-affinity LTB receptor . BLT exhibits
[107]
2
4
1