Page 52 - Read Online
P. 52
Page 14 of 24 Saier et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:43 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.87
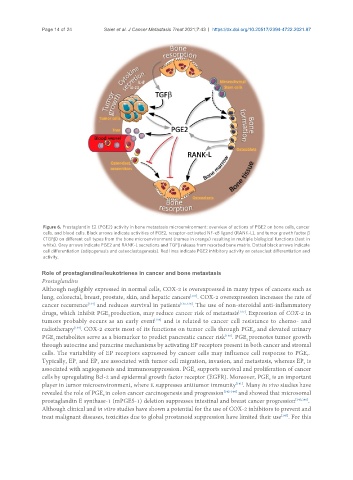
Figure 6. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) activity in bone metastasis microenvironment: overview of actions of PGE2 on bone cells, cancer
cells, and blood cells. Black arrows indicate activities of PGE2, receptor-activated NF-κB ligand (RANK-L), and tumor growth factor β
(TGFβ) on different cell types from the bone microenvironment (names in orange) resulting in multiple biological functions (text in
white). Grey arrows indicate PGE2 and RANK-L secretions and TGFβ release from resorbed bone matrix. Dotted black arrows indicate
cell differentiation (adipogenesis and osteoclastogenesis). Red lines indicate PGE2 inhibitory activity on osteoclast differentiation and
activity.
Role of prostaglandins/leukotrienes in cancer and bone metastasis
Prostaglandins
Although negligibly expressed in normal cells, COX-2 is overexpressed in many types of cancers such as
lung, colorectal, breast, prostate, skin, and hepatic cancers . COX-2 overexpression increases the rate of
[133]
[134]
cancer recurrence and reduces survival in patients [135,136] . The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs, which inhibit PGE production, may reduce cancer risk of metastasis . Expression of COX-2 in
[137]
2
[138]
tumors probably occurs as an early event and is related to cancer cell resistance to chemo- and
radiotherapy . COX-2 exerts most of its functions on tumor cells through PGE , and elevated urinary
[139]
2
PGE metabolites serve as a biomarker to predict pancreatic cancer risk . PGE promotes tumor growth
[140]
2
2
through autocrine and paracrine mechanisms by activating EP receptors present in both cancer and stromal
cells. The variability of EP receptors expressed by cancer cells may influence cell response to PGE .
2
Typically, EP and EP are associated with tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis, whereas EP is
2
1
4
associated with angiogenesis and immunosuppression. PGE supports survival and proliferation of cancer
2
cells by upregulating Bcl-2 and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Moreover, PGE is an important
2
player in tumor microenvironment, where it suppresses antitumor immunity . Many in vivo studies have
[141]
revealed the role of PGE in colon cancer carcinogenesis and progression [142-144] and showed that microsomal
2
prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) deletion suppresses intestinal and breast cancer progression [145,146] .
Although clinical and in vitro studies have shown a potential for the use of COX-2 inhibitors to prevent and
treat malignant diseases, toxicities due to global prostanoid suppression have limited their use . For this
[147]