Page 35 - Read Online
P. 35
Page 8 of 15 Pacheco et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:49 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.85
A C
B D
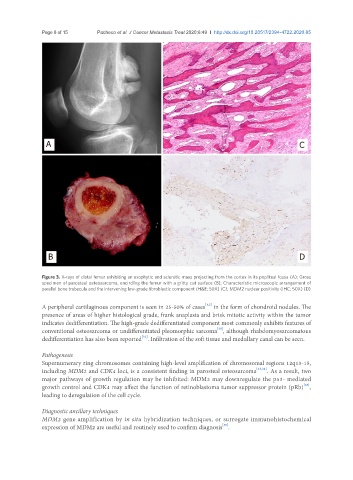
Figure 3. X-rays of distal femur exhibiting an exophytic and sclerotic mass projecting from the cortex in its popliteal fossa (A); Gross
specimen of parosteal osteosarcoma, encircling the femur with a gritty cut surface (B); Characteristic microscopic arrangement of
parallel bone trabecula and the intervening low-grade fibroblastic component (H&E; 50X) (C); MDM2 nuclear positivity (IHC; 50X) (D)
[1,2]
A peripheral cartilaginous component is seen in 25-50% of cases in the form of chondroid nodules. The
presence of areas of higher histological grade, frank anaplasia and brisk mitotic activity within the tumor
indicates dedifferentiation. The high-grade dedifferentiated component most commonly exhibits features of
[30]
conventional osteosarcoma or undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma , although rhabdomyosarcomatous
[32]
dedifferentiation has also been reported . Infiltration of the soft tissue and medullary canal can be seen.
Pathogenesis
Supernumerary ring chromosomes containing high-level amplification of chromosomal regions 12q13-15,
including MDM2 and CDK4 loci, is a consistent finding in parosteal osteosarcoma [33,34] . As a result, two
major pathways of growth regulation may be inhibited: MDM2 may downregulate the p53- mediated
[35]
growth control and CDK4 may affect the function of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (pRb) ,
leading to deregulation of the cell cycle.
Diagnostic ancillary techniques
MDM2 gene amplification by in situ hybridization techniques, or surrogate immunohistochemical
expression of MDM2 are useful and routinely used to confirm diagnosis .
[36]