Page 115 - Read Online
P. 115
Page 8 of 20 Vidoni et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:4 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.95
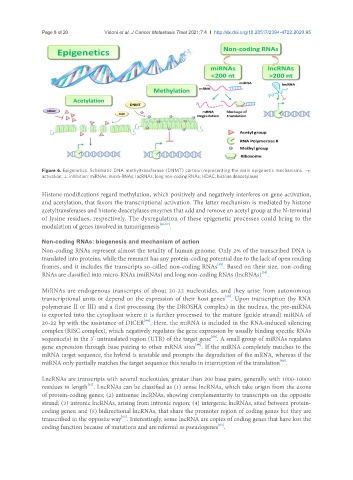
Figure 6. Epigenetics. Schematic DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) cartoon representing the main epigenetic mechanisms. →:
activation; ⊥: inhibition; miRNAs: micro-RNAs; lncRNAs; long non-coding RNAs; HDAC: histone deacetylases
Histone modifications regard methylation, which positively and negatively interferes on gene activation,
and acetylation, that favors the transcriptional activation. The latter mechanism is mediated by histone
acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases enzymes that add and remove an acetyl group at the N-terminal
of lysine residues, respectively. The dysregulation of these epigenetic processes could bring to the
modulation of genes involved in tumorigenesis [55-57] .
Non-coding RNAs: biogenesis and mechanism of action
Non-coding RNAs represent almost the totality of human genome. Only 2% of the transcribed DNA is
translated into proteins, while the remnant has any protein-coding potential due to the lack of open reading
[58]
frames, and it includes the transcripts so-called non-coding RNAs . Based on their size, non-coding
[58]
RNAs are classified into micro-RNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) .
MiRNAs are endogenous transcripts of about 20-22 nucleotides, and they arise from autonomous
[59]
transcriptional units or depend on the expression of their host genes . Upon transcription (by RNA
polymerase II or III) and a first processing (by the DROSHA complex) in the nucleus, the pre-miRNA
is exported into the cytoplasm where it is further processed to the mature (guide strand) miRNA of
[60]
20-22 bp with the assistance of DICER . Here, the miRNA is included in the RNA-induced silencing
complex (RISC complex), which negatively regulates the gene expression by usually binding specific RNAs
[60]
sequence(s) in the 3’-untranslated region (UTR) of the target gene . A small group of miRNAs regulates
[60]
gene expression through base pairing to other mRNA sites . If the miRNA completely matches to the
mRNA target sequence, the hybrid is unstable and prompts the degradation of the mRNA, whereas if the
[60]
miRNA only partially matches the target sequence this results in interruption of the translation .
LncRNAs are transcripts with several nucleotides, greater than 200 base pairs, generally with 1000-10000
residues in length . LncRNAs can be classified as (1) sense lncRNAs, which take origin from the exons
[61]
of protein-coding genes; (2) antisense lncRNAs, showing complementarity to transcripts on the opposite
strand; (3) intronic lncRNAs, arising from intronic region; (4) intergenic lncRNAs, sited between protein-
coding genes; and (5) bidirectional lncRNAs, that share the promoter region of coding genes but they are
transcribed in the opposite way . Interestingly, some lncRNA are copies of coding genes that have lost the
[62]
[63]
coding function because of mutations and are referred as pseudogenes .