Page 120 - Read Online
P. 120
Vidoni et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:4 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.95 Page 13 of 20
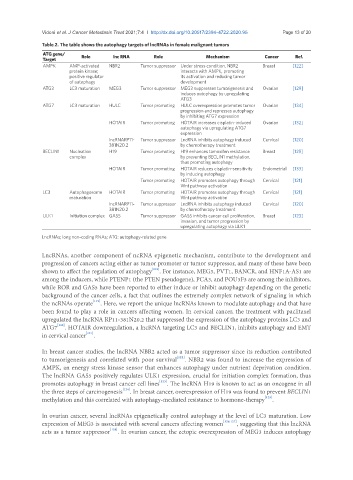
Table 2. The table shows the autophagy targets of lncRNAs in female malignant tumors
ATG gene/ Role lnc RNA Role Mechanism Cancer Ref.
Target
AMPK AMP-activated NBR2 Tumor suppressor Under stress condition, NBR2 Breast [122]
protein kinase; interacts with AMPK, promoting
positive regulator its activation and reducing tumor
of autophagy development
ATG3 LC3 maturation MEG3 Tumor suppressor MEG3 suppresses tumorigenesis and Ovarian [129]
induces autophagy by upregulating
ATG3
ATG7 LC3 maturation HULC Tumor promoting HULC overexpression promotes tumor Ovarian [134]
progression and represses autophagy
by inhibiting ATG7 expression
HOTAIR Tumor promoting HOTAIR increases cisplatin-induced Ovarian [132]
autophagy via upregulating ATG7
expression
lncRNARP11- Tumor suppressor LncRNA inhibits autophagy induced Cervical [120]
381N20.2 by chemotherapy treatment
BECLIN1 Nucleation H19 Tumor promoting H19 enhances tamoxifen resistance Breast [125]
complex by preventing BECLIN1 methylation,
thus promoting autophagy
HOTAIR Tumor promoting HOTAIR reduces cisplatin-sensitivity Endometrial [133]
by inducing autophagy
Tumor promoting HOTAIR promotes autophagy through Cervical [121]
Wnt pathway activation
LC3 Autophagosome HOTAIR Tumor promoting HOTAIR promotes autophagy through Cervical [121]
maturation Wnt pathway activation
lncRNARP11- Tumor suppressor LncRNA inhibits autophagy induced Cervical [120]
381N20.2 by chemotherapy treatment
ULK1 Initiation complex GAS5 Tumor suppressor GAS5 inhibits cancer cell proliferation, Breast [123]
invasion, and tumor progression by
upregulating autophagy via ULK1
LncRNAs; long non-coding RNAs; ATG: autophagy-related gene
LncRNAs, another component of ncRNA epigenetic mechanism, contribute to the development and
progression of cancers acting either as tumor promoter or tumor suppressor, and many of these have been
shown to affect the regulation of autophagy [119] . For instance, MEG3, PVT1, BANCR, and HNF1A-AS1 are
among the inducers, while PTENP1 (the PTEN pseudogene), PCA3, and POU3F3 are among the inhibitors,
while ROR and GAS5 have been reported to either induce or inhibit autophagy depending on the genetic
background of the cancer cells, a fact that outlines the extremely complex network of signaling in which
the ncRNAs operate [119] . Here, we report the unique lncRNAs known to modulate autophagy and that have
been found to play a role in cancers affecting women. In cervical cancer, the treatment with paclitaxel
upregulated the lncRNA RP11-381N20.2 that suppressed the expression of the autophagy proteins LC3 and
ATG7 [120] . HOTAIR downregulation, a lncRNA targeting LC3 and BECLIN1, inhibits autophagy and EMT
in cervical cancer [121] .
In breast cancer studies, the lncRNA NBR2 acted as a tumor suppressor since its reduction contributed
to tumorigenesis and correlated with poor survival [122] . NBR2 was found to increase the expression of
AMPK, an energy stress kinase sensor that enhances autophagy under nutrient deprivation condition.
The lncRNA GAS5 positively regulates ULK1 expression, crucial for initiation complex formation, thus
promotes autophagy in breast cancer cell lines [123] . The lncRNA H19 is known to act as an oncogene in all
the three steps of carcinogenesis [124] . In breast cancer, overexpression of H19 was found to prevent BECLIN1
methylation and this correlated with autophagy-mediated resistance to hormone-therapy [125] .
In ovarian cancer, several lncRNAs epigenetically control autophagy at the level of LC3 maturation. Low
expression of MEG3 is associated with several cancers affecting women [126,127] , suggesting that this lncRNA
acts as a tumor suppressor [128] . In ovarian cancer, the ectopic overexpression of MEG3 induces autophagy