Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Su et al. Intell Robot 2022;2(3):24474 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2022.17 Page 250
Table 1. Typical causality-based fairness notions
Type Fairness notion Formulation Description
The causal effects of the value change of
the sensitive attribute from to on
−
+
Total Effect [10] | ( | = ) − ( | = ) | ≤ decision = , where the intervention is
+
−
transmitted along all causal paths and is within
the fair threshold
The difference between the distribution of
Effect of treatment on | ( + | = ) − ( − | = ) | ≤ = had been and that of =
+
−
−
the treated [10] had been , given that had been
−
observed to be −
Group The causal effects of the value change of
the sensitive attribute from to on
−
+
Path-specific fairness [26,27] | ( | ( | , | ¯ )) − ( | ( )) | ≤
+
−
−
decision = along specific causal
paths, is within the fair threshold
It is satisfied when there is no directed path
No unresolved discrimination [28] - from sensitive attribute to outcome
allowed, except through a resolving variable
If it is satisfied, there is no path from the
No proxy discrimination [28] ( | ( = 0 )) = ( | ( = 1 )) sensitive attribute to the outcome blocked
∀ 0 , 1 ∈ ( )
by a proxy variable
An outcome achieves counterfactual fairness
towards an individual (i.e., O = o) if the
−
Counterfactual fairness [11] | ( + |O = o, = )− probability of = for such individual is
( − |O = o, = ) | ≤ the same as the probability of = for the
−
same individual, who belongs to a different
sensitive group
Individual It is based on situation testing where the
Individual direct discrimination [29] ( , ) = ∑ |X| | ( , ) · ( , ) | causal reasoning is used to define the
′
′
′
=1
distance function ( , ) ′
It detects discrimination by comparing the
effort required to reach the same level of
Equality of effort [30] Ψ + ( ) = Ψ − ( ) outcome of individuals from advantaged
where Ψ + ( ) = ∈ E[ + ] ⩾ and disadvantaged groups who are similar to
the target individual
It is a general fairness formalization for
representing various causality-based
Hybrid PC-fairness [31] | ( ˆ + | , − | ¯ |o) − ( ˆ − |o) | ≤
fairness notions, which is achieved
by differently tuning its parameters
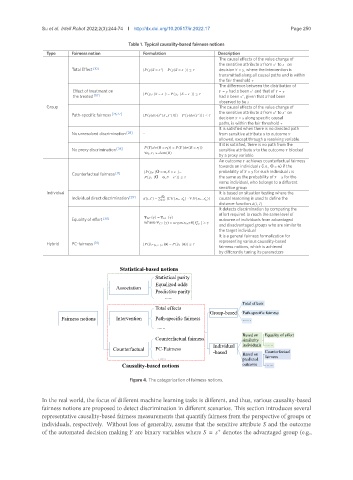
Statistical-based notions
Statistical parity
Equalized odds
Association
Predictive parity
......
Total effects
Total effects
Group-based Path-specific fairness
Fairness notions Intervention Path-specific fairness ······
......
Based on Equality of effort
Counterfactual fairness similarity
Individual individuals ······
Counterfactual PC-Fairness -based Counterfactual
...... Based on fairness
predicted
Causality-based notions outcome ······
Figure 4. The categorization of fairness notions.
In the real world, the focus of different machine learning tasks is different, and thus, various causality-based
fairness notions are proposed to detect discrimination in different scenarios. This section introduces several
representative causality-based fairness measurements that quantify fairness from the perspective of groups or
individuals, respectively. Without loss of generality, assume that the sensitive attribute and the outcome
of the automated decision making are binary variables where = denotes the advantaged group (e.g.,
+