Page 24 - Read Online
P. 24
He et al. Intell. Robot. 2025, 5(2), 313-32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2025.16 Page 323
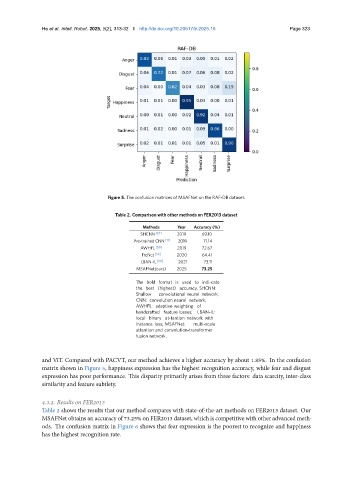
Figure 5. The confusion matrices of MSAFNet on the RAF-DB dataset.
Table 2. Comparison with other methods on FER2013 dataset
Methods Year Accuracy (%)
SHCNN [57] 2019 69.10
Pre-trained CNN [11] 2019 71.14
AWHFL [58] 2019 72.67
FreNet [59] 2020 64.41
LBAN-IL [60] 2021 73.11
MSAFNet(ours) 2025 73.25
The bold format is used to indi-cate
the best (highest) accuracy. SHCNN:
Shallow convolutional neural network;
CNN: convolution neural network;
AWHFL: adaptive weighting of
handcrafted feature losses; LBAN-IL:
local binary at-tention network with
instance loss; MSAFNet: multi-scale
attention and convolution-transformer
fusion network.
and ViT. Compared with PACVT, our method achieves a higher accuracy by about 1.85%. In the confusion
matrix shown in Figure 5, happiness expression has the highest recognition accuracy, while fear and disgust
expression has poor performance. This disparity primarily arises from three factors: data scarcity, inter-class
similarity and feature subtlety.
4.3.2. Results on FER2013
Table 2 shows the results that our method compares with state-of-the-art methods on FER2013 dataset. Our
MSAFNet obtains an accuracy of 73.25% on FER2013 dataset, which is competitive with other advanced meth-
ods. The confusion matrix in Figure 6 shows that fear expression is the poorest to recognize and happiness
has the highest recognition rate.