Page 20 - Read Online
P. 20
He et al. Intell. Robot. 2025, 5(2), 313-32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2025.16 Page 319
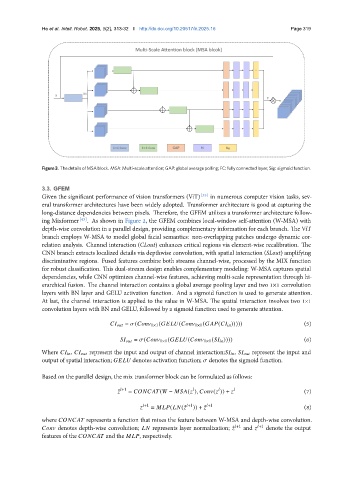
Figure 3. The details of MSA block. MSA: Multi-scale attention; GAP: global average polling; FC: fully connected layer; Sig: sigmoid function.
3.3. GFEM
Given the significant performance of vision transformers (ViT) [35] in numerous computer vision tasks, sev-
eral transformer architectures have been widely adopted. Transformer architecture is good at capturing the
long-distance dependencies between pixels. Therefore, the GFEM utilizes a transformer architecture follow-
ing Mixformer [43] . As shown in Figure 2, the GFEM combines local-window self-attention (W-MSA) with
depth-wise convolution in a parallel design, providing complementary information for each branch. The ViT
branch employs W-MSA to model global facial semantics: non-overlapping patches undergo dynamic cor-
relation analysis. Channel interaction (CLout) enhances critical regions via element-wise recalibration. The
CNN branch extracts localized details via depthwise convolution, with spatial interaction (SLout) amplifying
discriminative regions. Fused features combine both streams channel-wise, processed by the MIX function
for robust classification. This dual-stream design enables complementary modeling: W-MSA captures spatial
dependencies, while CNN optimizes channel-wise features, achieving multi-scale representation through hi-
erarchical fusion. The channel interaction contains a global average pooling layer and two 1×1 convolution
layers with BN layer and GELU activation function. And a sigmoid function is used to generate attention.
At last, the channel interaction is applied to the value in W-MSA. The spatial interaction involves two 1×1
convolution layers with BN and GELU, followed by a sigmoid function used to generate attention.
= ( 1×1 ( ( 1×1 ( ( ))))) (5)
= ( 1×1 ( ( 1×1 ( )))) (6)
Where , represent the input and output of channel interaction; , represent the input and
output of spatial interaction; denotes activation function; denotes the sigmoid function.
Based on the parallel design, the mix transformer block can be formulated as follows:
ˆ +1 = ( − ( ), ( )) + (7)
+1 = ( (ˆ +1 )) + ˆ +1 (8)
where represents a function that mixes the feature between W-MSA and depth-wise convolution.
denotes depth-wise convolution; represents layer normalization; ˆ +1 and +1 denote the output
features of the and the , respectively.