Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
He et al. Intell. Robot. 2025, 5(2), 313-32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2025.16 Page 327
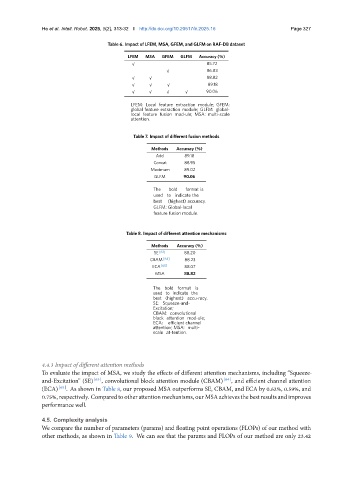
Table 6. Impact of LFEM, MSA, GFEM, and GLFM on RAF-DB dataset
LFEM MSA GFEM GLFM Accuracy (%)
√
85.72
√
86.83
√ √
88.82
√ √ √
89.18
√ √ √ √
90.06
LFEM: Local feature extraction module; GFEM:
global feature extraction module; GLFM: global-
local feature fusion mod-ule; MSA: multi-scale
attention.
Table 7. Impact of different fusion methods
Methods Accuracy (%)
Add 89.18
Concat 88.95
Maximum 89.02
GLFM 90.06
The bold format is
used to indicate the
best (highest) accuracy.
GLFM: Global-local
feature fusion module.
Table 8. Impact of different attention mechanisms
Methods Accuracy (%)
SE [63] 88.20
CBAM [64] 88.23
ECA [65] 88.07
MSA 88.82
The bold format is
used to indicate the
best (highest) accu-racy.
SE: Squeeze-and-
Excitation;
CBAM: convolutional
block attention mod-ule;
ECA: efficient channel
attention; MSA: multi-
scale at-tention.
4.4.3 Impact of different attention methods
To evaluate the impact of MSA, we study the effects of different attention mechanisms, including “Squeeze-
and-Excitation” (SE) [63] , convolutional block attention module (CBAM) [64] , and efficient channel attention
(ECA) [65] . As shown in Table 8, our proposed MSA outperforms SE, CBAM, and ECA by 0.62%, 0.59%, and
0.75%, respectively. Comparedtootherattentionmechanisms, ourMSAachievesthebestresultsandimproves
performance well.
4.5. Complexity analysis
We compare the number of parameters (params) and floating point operations (FLOPs) of our method with
other methods, as shown in Table 9. We can see that the params and FLOPs of our method are only 23.42