Page 27 - Read Online
P. 27
Page 326 He et al. Intell. Robot. 2025, 5(2), 313-32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2025.16
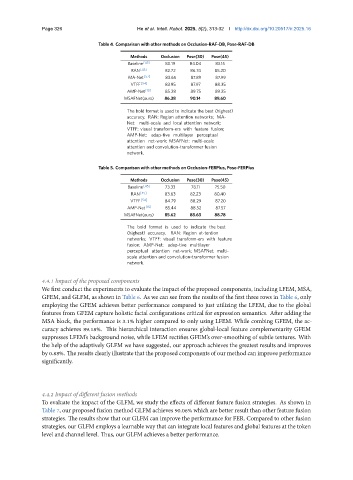
Table 4. Comparison with other methods on Occlusion-RAF-DB, Pose-RAF-DB
Methods Occlusion Pose(30) Pose(45)
Baseline [45] 80.19 84.04 83.15
RAN [45] 82.72 86.74 85.20
MA-Net [52] 83.65 87.89 87.99
VTFF [54] 83.95 87.97 88.35
AMP-Net [15] 85.28 89.75 89.25
MSAFNet(ours) 86.38 90.14 89.60
The bold format is used to indicate the best (highest)
accuracy. RAN: Region attention networks; MA-
Net: multi-scale and local attention network;
VTFF: visual transform-ers with feature fusion;
AMP-Net: adap-tive multilayer perceptual
attention net-work; MSAFNet: multi-scale
attention and convolution-transformer fusion
network.
Table 5. Comparison with other methods on Occlusion-FERPlus, Pose-FERPlus
Methods Occlusion Pose(30) Pose(45)
Baseline [45] 73.33 78.11 75.50
RAN [45] 83.63 82.23 80.40
VTFF [54] 84.79 88.29 87.20
AMP-Net [15] 85.44 88.52 87.57
MSAFNet(ours) 85.62 88.63 88.78
The bold format is used to indicate the best
(highest) accuracy. RAN: Region at-tention
networks; VTFF: visual transform-ers with feature
fusion; AMP-Net: adap-tive multilayer
perceptual attention net-work; MSAFNet: multi-
scale attention and convolution-transformer fusion
network.
4.4.1 Impact of the proposed components
We first conduct the experiments to evaluate the impact of the proposed components, including LFEM, MSA,
GFEM, and GLFM, as shown in Table 6. As we can see from the results of the first three rows in Table 6, only
employing the GFEM achieves better performance compared to just utilizing the LFEM, due to the global
features from GFEM capture holistic facial configurations critical for expression semantics. After adding the
MSA block, the performance is 3.1% higher compared to only using LFEM. While combing GFEM, the ac-
curacy achieves 89.18%. This hierarchical interaction ensures global-local feature complementarity GFEM
suppresses LFEM’s background noise, while LFEM rectifies GFEM’s over-smoothing of subtle textures. With
the help of the adaptively GLFM we have suggested, our approach achieves the greatest results and improves
by 0.88%. The results clearly illustrate that the proposed components of our method can improve performance
significantly.
4.4.2 Impact of different fusion methods
To evaluate the impact of the GLFM, we study the effects of different feature fusion strategies. As shown in
Table 7, our proposed fusion method GLFM achieves 90.06% which are better result than other feature fusion
strategies. The results show that our GLFM can improve the performance for FER. Compared to other fusion
strategies, our GLFM employs a learnable way that can integrate local features and global features at the token
level and channel level. Thus, our GLFM achieves a better performance.