Page 61 - Read Online
P. 61
Tong et al. Intell Robot 2024;4:125-45 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.08 Page 139
Figure 12. Comparison of joint4 torque data.
1.0
1.0
1.2
0.8
1.0
0.8
0.8 0.6
0.6
RMSE 0.6 MAE e R2 scor
0.4 0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
0.2
Fuzzy Control Fuzzy Control Fuzzy Control
Normal Control Normal Control Normal Control
0.0 0.0 0.0
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
Joint Joint Joint
2
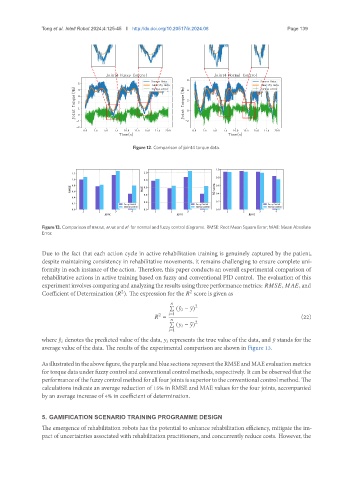
Figure 13. Comparison of , and for normal and fuzzy control diagrams. RMSE: Root Mean Square Error; MAE: Mean Absolute
Error.
Due to the fact that each action cycle in active rehabilitation training is genuinely captured by the patient,
despite maintaining consistency in rehabilitative movements, it remains challenging to ensure complete uni-
formity in each instance of the action. Therefore, this paper conducts an overall experimental comparison of
rehabilitative actions in active training based on fuzzy and conventional PID control. The evaluation of this
experimentinvolvescomparingandanalyzingtheresultsusingthreeperformancemetrics: , , and
2
Coefficient of Determination ( ). The expression for the score is given as
2
Í 2
( ˆ − ¯ )
2
= =1 (22)
Í 2
( − ¯ )
=1
where ˆ denotes the predicted value of the data, represents the true value of the data, and ¯ stands for the
average value of the data. The results of the experimental comparison are shown in Figure 13.
Asillustratedintheabovefigure,thepurpleandbluesectionsrepresenttheRMSEandMAEevaluationmetrics
for torque data under fuzzy control and conventional control methods, respectively. It can be observed that the
performanceofthefuzzycontrolmethodforallfourjointsissuperiortotheconventionalcontrolmethod. The
calculations indicate an average reduction of 15% in RMSE and MAE values for the four joints, accompanied
by an average increase of 4% in coefficient of determination.
5. GAMIFICATION SCENARIO TRAINING PROGRAMME DESIGN
The emergence of rehabilitation robots has the potential to enhance rehabilitation efficiency, mitigate the im-
pact of uncertainties associated with rehabilitation practitioners, and concurrently reduce costs. However, the