Page 42 - Read Online
P. 42
Sun et al. Intell Robot 2023;3(3):257-73 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2023.17 Page 269
(YXORWLRQ RI V H W N ZLWK SHULRG WUDQVPLVVLRQ
(YXORWLRQ RI V H W N RI 66 (7&
(YXORWLRQ RI V H W N LQ 6WDWLF (7&
W V
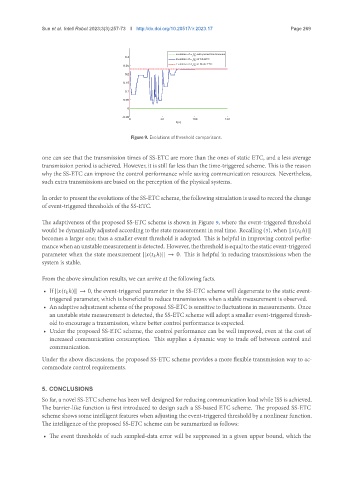
Figure 9. Evolutions of threshold comparisons.
one can see that the transmission times of SS-ETC are more than the ones of static ETC, and a less average
transmission period is achieved. However, it is still far less than the time-triggered scheme. This is the reason
why the SS-ETC can improve the control performance while saving communication resources. Nevertheless,
such extra transmissions are based on the perception of the physical systems.
In order to present the evolutions of the SS-ETC scheme, the following simulation is used to record the change
of event-triggered thresholds of the SS-ETC.
The adaptiveness of the proposed SS-ETC scheme is shown in Figure 9, where the event-triggered threshold
would be dynamically adjusted according to the state measurement in real time. Recalling (5), when || ( ℎ)||
becomes a larger one; thus a smaller event threshold is adopted. This is helpful in improving control perfor-
mancewhenanunstablemeasurementisdetected. However, thethresholdisequaltothestaticevent-triggered
parameter when the state measurement || ( ℎ)|| → 0. This is helpful in reducing transmissions when the
system is stable.
From the above simulation results, we can arrive at the following facts.
• If || ( ℎ)|| → 0, the event-triggered parameter in the SS-ETC scheme will degenerate to the static event-
triggered parameter, which is beneficial to reduce transmissions when a stable measurement is observed.
• An adaptive adjustment scheme of the proposed SS-ETC is sensitive to fluctuations in measurements. Once
an unstable state measurement is detected, the SS-ETC scheme will adopt a smaller event-triggered thresh-
old to encourage a transmission, where better control performance is expected.
• Under the proposed SS-ETC scheme, the control performance can be well improved, even at the cost of
increased communication consumption. This supplies a dynamic way to trade off between control and
communication.
Under the above discussions, the proposed SS-ETC scheme provides a more flexible transmission way to ac-
commodate control requirements.
5. CONCLUSIONS
So far, a novel SS-ETC scheme has been well designed for reducing communication load while ISS is achieved.
The barrier-like function is first introduced to design such a SS-based ETC scheme. The proposed SS-ETC
scheme shows some intelligent features when adjusting the event-triggered threshold by a nonlinear function.
The intelligence of the proposed SS-ETC scheme can be summarized as follows:
• The event thresholds of such sampled-data error will be suppressed in a given upper bound, which the