Page 281 - Read Online
P. 281
Magee et al. Egr1 in liver metabolism and cancer
Growth factors, stress, insulin
Adipose tissue
Insulin resistance Promote or inhibit?
PTEN/PI3K-AKT EGR1 HCC
GGPPS/MAPK Tumor suppressor
Obesity Downregulation in HCC
Inhibit tumor growth
Decrease energy expenditure Induce apoptosis
Promote inflammation Tumor promoter
promote drug resistance
Liver steatosis
Promote or inhibit? Liver regeneration
APAP-induced liver injury and fibrosis Promote cell-cycle
Induce cytokines
Promote acute injury
Inhibit chronic injury
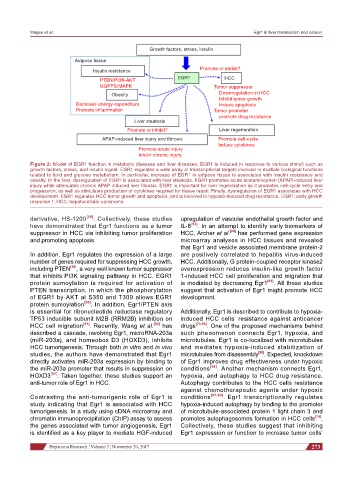
Figure 2: Model of EGR1 function in metabolic diseases and liver diseases. EGR1 is induced in response to various stimuli such as
growth factors, stress, and insulin signal. EGR1 regulates a wide array of transcriptional targets involved in multiple biological functions
related to lipid and glucose metabolism. In particular, increase of EGR1 in adipose tissue is associated with insulin resistance and
obesity. In the liver, dysregulation of EGR1 is associated with liver steatosis. EGR1 promotes acute acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver
injury while attenuates chronic APAP-induced liver fibrosis. EGR1 is important for liver regeneration as it promotes cell-cycle entry and
progression, as well as stimulates production of cytokines required for tissue repair. Finally, dysregulation of EGR1 associates with HCC
development. EGR1 regulates HCC tumor growth and apoptosis, and is involved in hypoxia-induced drug resistance. EGR1: early growth
response 1; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
derivative, HS-1200 [89] . Collectively, these studies upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and
have demonstrated that Egr1 functions as a tumor IL-8 [93] . In an attempt to identify early biomarkers of
suppressor in HCC via inhibiting tumor proliferation HCC, Archer et al. [94] has performed gene expression
and promoting apoptosis. microarray analyses in HCC tissues and revealed
that Egr1 and vesicle associated membrane protein-2
In addition, Egr1 regulates the expression of a large are positively correlated to hepatitis virus-induced
number of genes required for suppressing HCC growth, HCC. Additionally, G protein-coupled receptor kinase2
including PTEN [38] , a very well known tumor suppressor overexpression reduces insulin-like growth factor
that inhibits PI3K signaling pathway in HCC. EGR1 1-induced HCC cell proliferation and migration that
protein sumoylation is required for activation of is mediated by decreasing Egr1 [95] . All these studies
PTEN transcription, in which the phosphorylation suggest that activation of Egr1 might promote HCC
of EGR1 by AKT at S350 and T309 allows EGR1 development.
protein sumoylation [90] . In addition, Egr1/PTEN axis
is essential for ribonucleotide reductase regulatory Additionally, Egr1 is described to contribute to hypoxia-
TP53 inducible subunit M2B (RRM2B) inhibition on induced HCC cells’ resistance against anticancer
HCC cell migration [91] . Recently, Wang et al. [92] has drugs [74,96] . One of the proposed mechanisms behind
described a cascade, involving Egr1, microRNA-203a such phenomenon connects Egr1, hypoxia, and
(miR-203a), and homeobox D3 (HOXD3), inhibits microtubules. Egr1 is co-localized with microtubules
HCC tumorigenesis. Through both in vitro and in vivo and mediates hypoxia-induced stabilization of
[96]
studies, the authors have demonstrated that Egr1 microtubules from disassembly . Expected, knockdown
directly activates miR-203a expression by binding to of Egr1 improves drug effectiveness under hypoxic
the miR-203a promoter that results in suppression on conditions [96] . Another mechanism connects Egr1,
HOXD3 [92] . Taken together, these studies support an hypoxia, and autophagy to HCC drug resistance.
anti-tumor role of Egr1 in HCC. Autophagy contributes to the HCC cells resistance
against chemotherapeutic agents under hypoxic
Contrasting the anti-tumorigenic role of Egr1 is conditions [97-99] . Egr1 transcriptionally regulates
study indicating that Egr1 is associated with HCC hypoxia-induced autophagy by binding to the promoter
tumorigenesis. In a study using cDNA microarray and of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 and
chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay to assess promotes autophagosomes formation in HCC cells [74] .
the genes associated with tumor angiogenesis, Egr1 Collectively, these studies suggest that inhibiting
is identified as a key player to mediate HGF-induced Egr1 expression or function to increase tumor cells’
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ November 20, 2017 273