Page 272 - Read Online
P. 272
Lecchini et al. HCC vascular invasion in sorafenib treatment
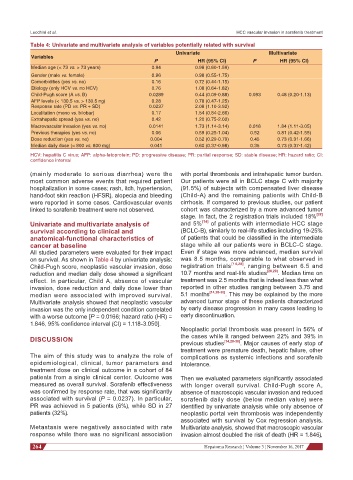
Table 4: Univariate and multivariate analysis of variables potentially related with survival
Univariate Multivariate
Variables
P HR (95% CI) P HR (95% CI)
Median age (< 73 vs. > 73 years) 0.94 0.98 (0.60-1.59)
Gender (male vs. female) 0.96 0.98 (0.55-1.75)
Comorbidities (yes vs. no) 0.16 0.72 (0.44-1.15)
Etiology (only HCV vs. no HCV) 0.76 1.08 (0.64-1.82)
Child-Pugh score (A vs. B) 0.0289 0.44 (0.09-0.88) 0.093 0.48 (0.20-1.13)
AFP levels (< 130.5 vs. > 130.5 ng) 0.28 0.78 (0.47-1.25)
Response rate (PD vs. PR + SD) 0.0237 2.08 (1.10-3.92)
Localitation (mono vs. bilobar) 0.17 1.54 (0.84-2.66)
Extrahepatic spread (yes vs. no) 0.42 1.20 (0.75-2.00)
Macrovascular invasion (yes vs. no) 0.0141 1.73 (1.14-3.14) 0.016 1.84 (1.11-3.05)
Previous therapies (yes vs. no) 0.06 0.59 (0.25-1.04) 0.52 0.81 (0.42-1.55)
Dose reduction (yes vs. no) 0.004 0.52 (0.29-0.79) 0.45 0.73 (0.31-1.66)
Median daily dose (< 800 vs. 800 mg) 0.041 0.60 (0.37-0.98) 0.35 0.73 (0.37-1.42)
HCV: hepatitis C virus; AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; PD: progressive disease; PR: partial response; SD: stable disease; HR: hazard ratio; CI:
confidence interval
(mainly moderate to serious diarrhea) were the with portal thrombosis and intrahepatic tumor burden.
most common adverse events that required patient Our patients were all in BCLC stage C with majority
hospitalization in some cases; rash, itch, hypertension, (91.5%) of subjects with compensated liver disease
hand-foot skin reaction (HFSR), alopecia and bleeding (Child-A) and the remaining patients with Child-B
were reported in some cases. Cardiovascular events cirrhosis. If compared to previous studies, our patient
linked to sorafenib treatment were not observed. cohort was characterized by a more advanced tumor
stage. In fact, the 2 registration trials included 18% [28]
Univariate and multivariate analysis of and 5% [14] of patients with intermediate HCC stage
survival according to clinical and (BCLC-B), similarly to real-life studies including 19-25%
anatomical-functional characteristics of of patients that could be classified in the intermediate
cancer at baseline stage while all our patients were in BCLC-C stage.
All studied parameters were evaluated for their impact Even if stage was more advanced, median survival
on survival. As shown in Table 4 by univariate analysis: was 8.5 months, comparable to what observed in
Child-Pugh score, neoplastic vascular invasion, dose registration trials [14,28] , ranging between 6.5 and
reduction and median daily dose showed a significant 10.7 months and real-life studies [28,29] . Median time on
effect. In particular, Child A, absence of vascular treatment was 2.5 months that is indeed less than what
invasion, dose reduction and daily dose lower than reported in other studies ranging between 3.75 and
median were associated with improved survival. 5.1 months [14,28-30] . This may be explained by the more
Multivariate analysis showed that neoplastic vascular advanced tumor stage of these patients characterized
invasion was the only independent condition correlated by early disease progression in many cases leading to
with a worse outcome [P = 0.0166; hazard ratio (HR) = early discontinuation.
1.846, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.118-3.050].
Neoplastic portal thrombosis was present in 56% of
DISCUSSION the cases while it ranged between 22% and 39% in
previous studies [14,28-30] . Major causes of early stop of
treatment were premature death, hepatic failure, other
The aim of this study was to analyze the role of complications as systemic infections and sorafenib
epidemiological, clinical, tumor parameters and intolerance.
treatment dose on clinical outcome in a cohort of 84
patients from a single clinical center. Outcome was Then we evaluated parameters significantly associated
measured as overall survival. Sorafenib effectiveness with longer overall survival. Child-Pugh score A,
was confirmed by response rate, that was significantly absence of macroscopic vascular invasion and reduced
associated with survival (P = 0.0237). In particular, sorafenib daily dose (below median value) were
PR was achieved in 5 patients (6%), while SD in 27 identified by univariate analysis while only absence of
patients (32%). neoplastic portal vein thrombosis was independently
associated with survival by Cox regression analysis.
Metastasis were negatively associated with rate Multivariate analysis, showed that macroscopic vascular
response while there was no significant association invasion almost doubled the risk of death (HR = 1.846),
264 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ November 16, 2017