Page 122 - Read Online
P. 122
Gomaa et al. Advanced HCC: current and potential therapies
impair the effect of sorafenib on tumor progression and with median TTP of 12.8 months and median OS
interfere with possible survival improvement. [18] of 18.7 months. The most common adverse events
observed with lenvatinib were hypertension, diarrhea,
Eventually 60-70% of patients with advanced HCC anorexia, weight loss, and fatigue. [30]
progress on sorafenib. The pattern of progression on
sorafenib has been identified as a predictor of post- Lenvatinib was investigated as first line therapy
progression survival. [26,27] The development of new compared to sorafenib in a multicenter, randomized,
extra-hepatic lesion, vascular invasion, and worsening open-label, phase III trial that included 954 patients
performance status on therapy were associated with with intermediate or advanced stage HCC. The OS
the poorest prognosis. with lenvatinib was non-inferior to sorafenib, and PFS,
TTP, and objective response rate (ORR) significantly
For patients in advanced-stage who progress on or improved with lenvatinib (NCT01761266). [31] Lenvatinib
cannot tolerate sorafenib, management options are thus is the first agent to show results that are equal
limited, and a large unmet need still exists. However, or better than sorafenib in advanced stage HCC, and
results of trials with lenvatinib as first line therapy [28] might become an alternative to sorafenib as first line
and regorafenib [29] and immunotherapy as effective treatment.
second line treatments are promising.
Second-line therapy
Other molecular targeted agents Figure 2 shows OS of second line therapies compared
First-line therapy to sorafenib. [29,32-34] Regorafenib, a multi-kinase inhibitor
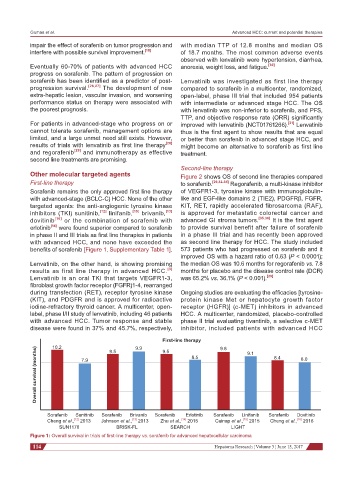
Sorafenib remains the only approved first line therapy of VEGFR1-3, tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin-
with advanced-stage (BCLC-C) HCC. None of the other like and EGF-like domains 2 (TIE2), PDGFRβ, FGFR,
targeted agents: the anti-angiogenic tyrosine kinase KIT, RET, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (RAF),
inhibitors (TKI) sunitinib, [12] linifanib, [15] brivanib, [13] is approved for metastatic colorectal cancer and
dovitinib [16] or the combination of sorafenib with advanced GI stroma tumors. [35,36] It is the first agent
erlotinib [14] were found superior compared to sorafenib to provide survival benefit after failure of sorafenib
in phase II and III trials as first line therapies in patients in a phase III trial and has recently been approved
with advanced HCC, and none have exceeded the as second line therapy for HCC. The study included
benefits of sorafenib [Figure 1, Supplementary Table 1]. 573 patients who had progressed on sorafenib and it
improved OS with a hazard ratio of 0.63 (P < 0.0001);
Lenvatinib, on the other hand, is showing promising the median OS was 10.6 months for regorafenib vs. 7.8
[3]
results as first line therapy in advanced HCC. months for placebo and the disease control rate (DCR)
Lenvatinib is an oral TKI that targets VEGFR1-3, was 65.2% vs. 36.1% (P < 0.001). [29]
fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR)1-4, rearranged
during transfection (RET), receptor tyrosine kinase Ongoing studies are evaluating the efficacies [tyrosine-
(KIT), and PDGFR and is approved for radioactive protein kinase Met or hepatocyte growth factor
iodine-refractory thyroid cancer. A multicenter, open- receptor (HGFR)] (c-MET) inhibitors in advanced
label, phase I/II study of lenvatinib, including 46 patients HCC. A multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled
with advanced HCC. Tumor response and stable phase II trial evaluating tivantinib, a selective c-MET
disease were found in 37% and 45.7%, respectively, inhibitor, included patients with advanced HCC
First-line therapy 9.8 9.1
10.2
9.9
Overall survival (months) 7.9 8.4 8.0
9.5
9.5
8.5
Sorafenib Sunitinib Sorafenib Brivanib Sorafenib Erlotinib Sorafenib Linifanib Sorafenib Dovitinib
[16]
[14]
[15]
[12]
[13]
Cheng et al., 2013 Johnson et al., 2013 Zhu et al., 2015 Cainap et al., 2015 Cheng et al., 2016
SUN1170 BRISK-FL SEARCH LIGHT
Figure 1: Overall survival in trials of first-line therapy vs. sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
114 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ June 15, 2017