Page 328 - Read Online
P. 328
Loria et al. CEUS in evaluation of vascularization of HCC
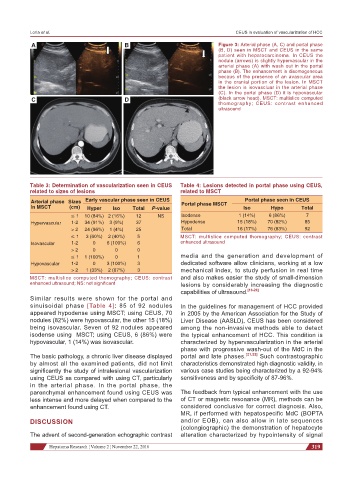
A B Figure 3: Arterial phase (A, C) and portal phase
(B, D) seen in MSCT and CEUS in the same
patient with hepatocarcinoma. In CEUS the
nodule (arrows) is slightly hypervascular in the
arterial phase (A) with wash out in the portal
phase (B). The enhancement is disomogeneous
becaus of the presence of an avascular area
in the cranial portion of the lesion. In MSCT
the lesion is isovascluar in the arterial phase
(C). In the portal phase (D) it is hypovascular
C D (black arrow head). MSCT: multislice computed
thomography; CEUS: contrast enhanced
ultrasound
Table 3: Determination of vascularization seen in CEUS Table 4: Lesions detected in portal phase using CEUS,
related to sizes of lesions related to MSCT
Arterial phase Sizes Early vascular phase seen in CEUS Portal phase MSCT Portal phase seen in CEUS
in MSCT (cm) Hyper Iso Total P-value Iso Hypo Total
≤ 1 10 (84%) 2 (16%) 12 NS Isodense 1 (14%) 6 (86%) 7
Hypervascular 1-2 34 (91%) 3 (9%) 37 Hypodense 15 (18%) 70 (82%) 85
> 2 24 (96%) 1 (4%) 25 Total 16 (17%) 76 (83%) 92
≤ 1 3 (60%) 2 (40%) 5 MSCT: multislice computed thomography; CEUS: contrast
Isovascular 1-2 0 6 (100%) 6 enhanced ultrasound
> 2 0 0 0
≤ 1 1 (100%) 0 1 media and the generation and development of
Hypovascular 1-2 0 3 (100%) 3 dedicated software allow clinicians, working at a low
> 2 1 (33%) 2 (67%) 3 mechanical index, to study perfusion in real time
MSCT: multislice computed thomography; CEUS: contrast and also makes easier the study of small-dimension
enhanced ultrasound; NS: not significant lesions by considerably increasing the diagnostic
capabilities of ultrasound. [16-20]
Similar results were shown for the portal and
sinuisoidal phase [Table 4]: 85 of 92 nodules In the guidelines for management of HCC provided
appeared hypodense using MSCT; using CEUS, 70 in 2005 by the American Association for the Study of
nodules (82%) were hypovascular, the other 15 (18%) Liver Disease (AASLD), CEUS has been considered
being isovascular. Seven of 92 nodules appeared among the non-invasive methods able to detect
isodense using MSCT; using CEUS, 6 (86%) were the typical enhancement of HCC. This condition is
hypovascular, 1 (14%) was isovascular. characterized by hypervascularization in the arterial
phase with progressive wash-out of the MdC in the
The basic pathology, a chronic liver disease displayed portal and late phases. [21,22] Such contrastographic
by almost all the examined patients, did not limit characteristics demonstrated high diagnostic validity, in
significantly the study of intralesional vascularization various case studies being characterized by a 92-94%
using CEUS as compared with using CT, particularly sensitiveness and by specificity of 87-96%.
in the arterial phase. In the portal phase, the
parenchymal enhancement found using CEUS was The feedback from typical enhancement with the use
less intense and more delayed when compared to the of CT or magnetic resonance (MR), methods can be
enhancement found using CT. considered conclusive for correct diagnosis. Also,
MR, if performed with hepatospecific MdC (BOPTA
DISCUSSION and/or EOB), can also allow in late sequences
(colongiographic) the demonstration of hepatocyte
The advent of second-generation echographic contrast alteration characterized by hypointensity of signal
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 2 ¦ November 22, 2016 319