Page 293 - Read Online
P. 293
Butt et al. TAE for ruptured HCC in Pakistan
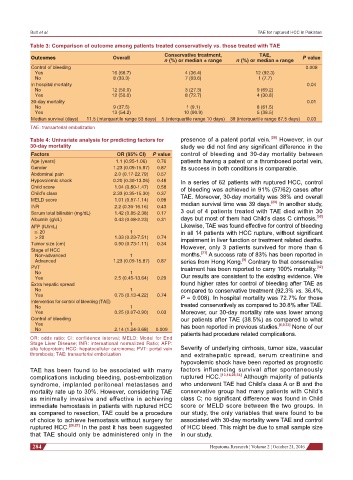
Table 3: Comparison of outcome among patients treated conservatively vs. those treated with TAE
Conservative treatment, TAE,
Outcomes Overall P value
n (%) or median ± range n (%) or median ± range
Control of bleeding 0.008
Yes 16 (66.7) 4 (36.4) 12 (92.3)
No 8 (33.3) 7 (63.6) 1 (7.7)
In hospital mortality 0.04
No 12 (50.0) 3 (27.3) 9 (69.2)
Yes 12 (50.0) 8 (72.7) 4 (30.8)
30-day mortality 0.01
No 9 (37.5) 1 (9.1) 8 (61.5)
Yes 13 (54.2) 10 (90.9) 5 (38.5)
Median survival (days) 11.5 (interquartile range 53 days) 5 (interquartile range 10 days) 39 (interquartile range 87.5 days) 0.03
TAE: transarterial embolization
Table 4: Univariate analysis for predicting factors for presence of a patent portal vein. [28] However, in our
30-day mortality study we did not find any significant difference in the
Factors OR (95% CI) P value control of bleeding and 30-day mortality between
Age (years) 1.1 (0.95-1.06) 0.76 patients having a patent or a thrombosed portal vein,
Gender 1.23 (0.09-15.87) 0.87 its success in both conditions is comparable.
Abdominal pain 2.0 (0.17-22.79) 0.57
Hypovolemic shock 0.20 (0.30-13.06) 0.46 In a series of 62 patients with ruptured HCC, control
Child score 1.04 (0.80-1.47) 0.58 of bleeding was achieved in 91% (57/62) cases after
Child’s class 2.33 (0.35-15.30) 0.37 TAE. Moreover, 30-day mortality was 38% and overall
MELD score 1.01 (0.87-1.14) 0.98 [29]
INR 2.2 (0.30-16.16) 0.43 median survival time was 39 days. In another study,
Serum total bilirubin (mg/dL) 1.42 (0.85-2.38) 0.17 3 out of 4 patients treated with TAE died within 30
[30]
Albumin (g/dL) 0.43 (0.08-2.23) 0.31 days but most of them had Child’s class C cirrhosis.
AFP (IU/mL) Likewise, TAE was found effective for control of bleeding
≤ 20 1 in all 14 patients with HCC rupture, without significant
> 20 1.33 (0.23-7.51) 0.74 impairment in liver function or treatment related deaths.
Tumor size (cm) 0.90 (0.73-1.11) 0.34
Stage of HCC However, only 3 patients survived for more than 6
[31]
Non-advanced 1 months. A success rate of 83% has been reported in
[9]
Advanced 1.23 (0.09-15.87) 0.87 series from Hong Kong. Contrary to that conservative
PVT treatment has been reported to carry 100% mortality.
[32]
No 1
Yes 2.5 (0.45-13.64) 0.29 Our results are consistent to the existing evidence. We
Extra hepatic spread found higher rates for control of bleeding after TAE as
No 1 compared to conservative treatment (92.3% vs. 36.4%,
Yes 0.75 (0.13-4.22) 0.74 P = 0.008). In hospital mortality was 72.7% for those
Intervention for control of bleeding (TAE)
No 1 treated conservatively as compared to 30.8% after TAE.
Yes 0.25 (0.07-0.90) 0.03 Moreover, our 30-day mortality rate was lower among
Control of bleeding our patients after TAE (38.5%) as compared to what
Yes 1 has been reported in previous studies. [6,9,33] None of our
No 2.14 (1.24-3.68) 0.009
patients had procedure related complications.
OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; MELD: Model for End
Stage Liver Disease; INR: international normalized Ratio; AFP:
alfa fetoprotein; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; PVT: portal vein Severity of underlying cirrhosis, tumor size, vascular
thrombosis; TAE: transarterial embolization and extrahepatic spread, serum creatinine and
hypovolemic shock have been reported as prognostic
TAE has been found to be associated with many factors influencing survival after spontaneously
complications including bleeding, post-embolization ruptured HCC. [13,14,29,34] Although majority of patients
syndrome, implanted peritoneal metastases and who underwent TAE had Child’s class A or B and the
mortality rate up to 30%. However, considering TAE conservative group had many patients with Child’s
as minimally invasive and effective in achieving class C; no significant difference was found in Child
immediate hemostasis in patients with ruptured HCC score or MELD score between the two groups. In
as compared to resection, TAE could be a procedure our study, the only variables that were found to be
of choice to achieve hemostasis without surgery for associated with 30-day mortality were TAE and control
ruptured HCC. [26,27] In the past it has been suggested of HCC bleed. This might be due to small sample size
that TAE should only be administered only in the in our study.
284 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 2 ¦ October 21, 2016