Page 208 - Read Online
P. 208
publication of this phase I data, a multi-institutional phase circulation is isolated via a special patented double balloon
III random assignment control trial was started in 2005, catheter directed via venous cannulation and fluoroscopically
where PHP with melphalan was compared with the current guided placement in the IVC (Delcath Catheter Systems,
best available care (systemic chemotherapy, embolization, Delcath Inc., New York, NY). This allows for capture of the
supportive care) in patients with metastatic melanoma with chemotherapy-laden effluent from the liver, which is filtered
[3]
the majority of tumor contained in the liver. This trial via veno-venous bypass prior to returning to the systemic
was completed in 2010 and the results have recently been circulation. PHP takes advantage of the tumor blood
[3,8]
published, with analysis showing an increase in hepatic supply in which 90% of the tumor is supplied by hepatic artery
progression-free survival in the melphalan PHP arm compared inflow. In contrast, normal hepatocytes receive over 50% of
[9]
to the best available care. Currently, there are numerous their blood flow from the portal venous inflow. By isolating
centers throughout the world evaluating PHP and improving the hepatic arteries, infusion of chemotherapeutic agents
the technical aspects and treatment outcomes. are able to take the most direct circulatory pathway to liver
tumors while somewhat sparing normal hepatocytes. It is
Evaluation critical to ensure that flow is isolated to the liver to avoid
We evaluated data using previous publications on methods inadvertent chemoperfusion of non-target organs. Once the
of liver perfusion, ranging from reviews to clinical trials. agent has completed its hepatic circulation, it is collected via
An initial PubMed search with the keyword “percutaneous fenestrations situated between patented double balloons
hepatic perfusion” was performed yielding 135 publications. of the catheter, from the hepatic veins as it enters the IVC.
Publications were excluded if they were not in English, had This catheter is initially placed and tested under fluoroscopy
no mention of liver metastasis or liver tumors, or were not in the retrohepatic IVC so that the balloons are carefully
available online or through an easily accessible source. We seated cephalad and caudad to the hepatic veins. The blood
then screened 25 publications relating to PHP using the is then directed through an extracorporeal filtration system
addition of the keyword “melphalan”. This search yielded (containing activated charcoal filter cartridges) which removes
17 publications, only those that linked or contained primary the agent prior to return to the systemic circulation via an
data relating to PHP or IHP were selected, and ultimately 16 internal jugular venous catheter [Figure 1].
publications contributed to this review.
The procedure is usually performed using general anesthesia
TECHNICAL ASPECTS with arterial line access placed for blood pressure monitoring,
as well as internal jugular venous access for infusion from
Procedure the veno-venous bypass circuit. The extracorporeal pump is
As mentioned previously, PHP is a technique where a primed with normal saline, and during the procedure, heparin
chemotherapeutic or biologic agent is delivered via is administered to maintain an activated clotting time at
catheterization of the hepatic artery. The hepatic venous therapeutic levels. Percutaneous access of the right common
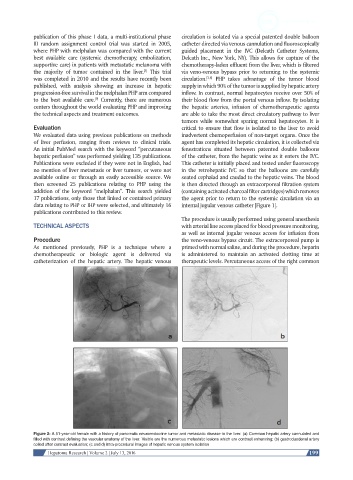
Figure 2: A 51-year-old female with a history of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and metastatic disease to the liver. (a) Common hepatic artery cannulated and
filled with contrast defining the vascular anatomy of the liver. Visible are the numerous metastatic lesions which are contrast enhancing; (b) gastroduodenal artery
coiled after contrast evaluation; (c and d) intra-procedural images of hepatic venous system isolation
Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | July 13, 2016 199