Page 113 - Read Online
P. 113
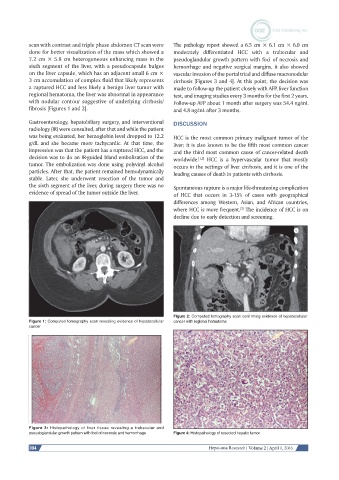
scan with contrast and triple phase abdomen CT scan were The pathology report showed a 6.5 cm × 6.1 cm × 6.0 cm
done for better visualization of the mass which showed a moderately differentiated HCC with a trabecular and
7.2 cm × 5.8 cm heterogeneous enhancing mass in the pseudoglandular growth pattern with foci of necrosis and
sixth segment of the liver, with a pseudocapsule bulges hemorrhage and negative surgical margins, it also showed
on the liver capsule, which has an adjacent small 6 cm × vascular invasion of the portal triad and diffuse macronodular
3 cm accumulation of complex fluid that likely represents cirrhosis [Figures 3 and 4]. At this point, the decision was
a ruptured HCC and less likely a benign liver tumor with made to follow-up the patient closely with AFP, liver function
regional hematoma, the liver was abnormal in appearance test, and imaging studies every 3 months for the first 2 years.
with nodular contour suggestive of underlying cirrhosis/ Follow-up AFP about 1 month after surgery was 54.4 ng/mL
fibrosis [Figures 1 and 2]. and 4.8 ng/mL after 3 months.
Gastroenterology, hepatobiliary surgery, and interventional DISCUSSION
radiology (IR) were consulted, after that and while the patient
was being evaluated, her hemoglobin level dropped to 12.2 HCC is the most common primary malignant tumor of the
g/dL and she became more tachycardic. At that time, the liver; it is also known to be the fifth most common cancer
impression was that the patient has a ruptured HCC, and the and the third most common cause of cancer-related death
decision was to do an IR-guided bland embolization of the worldwide. HCC is a hypervascular tumor that mostly
[1,2]
tumor. The embolization was done using polyvinyl alcohol occurs in the settings of liver cirrhosis, and it is one of the
particles. After that, the patient remained hemodynamically leading causes of death in patients with cirrhosis.
stable. Later, she underwent resection of the tumor and
the sixth segment of the liver, during surgery there was no Spontaneous rupture is a major life-threatening complication
evidence of spread of the tumor outside the liver. of HCC that occurs in 3-15% of cases with geographical
differences among Western, Asian, and African countries,
where HCC is more frequent. The incidence of HCC is on
[3]
decline due to early detection and screening.
Figure 2: Computed tomography scan confirming evidence of hepatocellular
Figure 1: Computed tomography scan revealing evidence of hepatocellular cancer with regional hematoma
cancer
Figure 3: Histopathology of liver tissue revealing a trabecular and
pseudoglandular growth pattern with foci of necrosis and hemorrhage Figure 4: Histopathology of resected hepatic tumor
104 Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | April 1, 2016