Page 64 - Read Online
P. 64
Page 8 of 14 Schwertheim et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:41 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.23
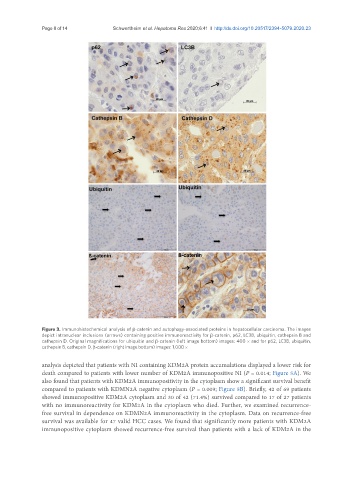
Figure 3. Immunohistochemical analysis of β-catenin and autophagy-associated proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma. The images
depict intranuclear inclusions (arrows) containing positive immunoreactivity for β-catenin, p62, LC3B, ubiquitin, cathepsin B and
cathepsin D. Original magnifications for ubiquitin and β-catenin (left image bottom) images: 400 × and for p62, LC3B, ubiquitin,
cathepsin B, cathepsin D, β-catenin (right image bottom) images: 1,000 ×
analysis depicted that patients with NI containing KDM2A protein accumulations displayed a lower risk for
death compared to patients with lower number of KDM2A immunopositive NI (P = 0.014; Figure 5A). We
also found that patients with KDM2A immunopositivity in the cytoplasm show a significant survival benefit
compared to patients with KDMN2A negative cytoplasm (P = 0.009; Figure 5B). Briefly, 42 of 69 patients
showed immunopositive KDM2A cytoplasm and 30 of 42 (71.4%) survived compared to 17 of 27 patients
with no immunoreactivity for KDM2A in the cytoplasm who died. Further, we examined recurrence-
free survival in dependence on KDMN2A immunoreactivity in the cytoplasm. Data on recurrence-free
survival was available for 47 valid HCC cases. We found that significantly more patients with KDM2A
immunopositive cytoplasm showed recurrence-free survival than patients with a lack of KDM2A in the