Page 95 - Read Online
P. 95
Karademir. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:58 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.40 Page 5 of 18
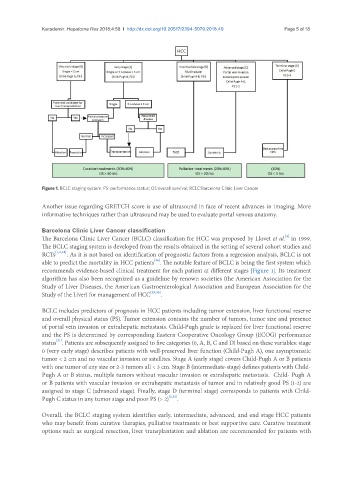
Figure 1. BCLC staging system. PS: performance status; OS:overall survival; BCLC:Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer
Another issue regarding GRETCH score is use of ultrasound in face of recent advances in imaging. More
informative techniques rather than ultrasound may be used to evaluate portal venous anatomy.
Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer classification
[3]
The Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) classification for HCC was proposed by Llovet et al. in 1999.
The BCLC staging system is developed from the results obtained in the setting of several cohort studies and
RCTs [1,3,28] . As it is not based on identification of prognostic factors from a regression analysis, BCLC is not
[26]
able to predict the mortality in HCC patients . The notable feature of BCLC is being the first system which
recommends evidence-based clinical treatment for each patient at different stages [Figure 1]. Its treatment
algorithm has also been recognized as a guideline by renown societies (the American Association for the
Study of Liver Diseases, the American Gastroenterological Association and European Association for the
Study of the Liver) for management of HCC [29,30] .
BCLC includes predictors of prognosis in HCC patients including tumor extension, liver functional reserve
and overall physical status (PS). Tumor extension contains the number of tumors, tumor size and presence
of portal vein invasion or extrahepatic metastasis. Child-Pugh grade is replaced for liver functional reserve
and the PS is determined by corresponding Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance
[31]
status . Patients are subsequently assigned to five categories (0, A, B, C and D) based on these variables: stage
0 (very early stage) describes patients with well-preserved liver function (Child-Pugh A), one asymptomatic
tumor < 2 cm and no vascular invasion or satellites. Stage A (early stage) covers Child-Pugh A or B patients
with one tumor of any size or 2-3 tumors all < 3 cm. Stage B (intermediate-stage) defines patients with Child-
Pugh A or B status, multiple tumors without vascular invasion or extrahepatic metastasis. Child- Pugh A
or B patients with vascular invasion or extrahepatic metastasis of tumor and in relatively good PS (1-2) are
assigned to stage C (advanced stage). Finally, stage D (terminal stage) corresponds to patients with Child-
Pugh C status in any tumor stage and poor PS (> 2) [3,32] .
Overall, the BCLC staging system identifies early, intermediate, advanced, and end stage HCC patients
who may benefit from curative therapies, palliative treatments or best supportive care. Curative treatment
options such as surgical resection, liver transplantation and ablation are recommended for patients with