Page 94 - Read Online
P. 94
Page 4of 18 Karademir. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:58 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.40
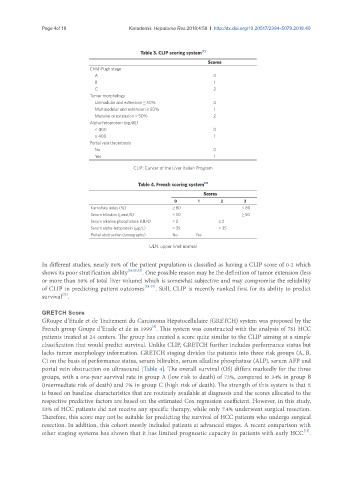
Table 3. CLIP scoring system [7]
Scores
Child-Pugh stage
A 0
B 1
C 2
Tumor morphology
Uninodular and extension ≤ 50% 0
Multinodular and extension ≤ 50% 1
Massive or extension > 50% 2
Alpha-fetoprotein (ng/dL)
< 400 0
≥ 400 1
Portal vein thrombosis
No 0
Yes 1
CLIP: Cancer of the Liver Italian Program
Table 4. French scoring system [8]
Scores
0 1 2 3
Karnofsky index (%) ≥ 80 < 80
Serum bilirubin (μmol/L) < 50 ≥ 50
Serum alkaline phosphatase (ULN) < 2 ≥ 2
Serum alpha-fetoprotein (μg/L) < 35 > 35
Portal obstruction (sonography) No Yes
ULN: upper limit normal
In different studies, nearly 80% of the patient population is classified as having a CLIP score of 0-2 which
shows its poor stratification ability [18,22,23] . One possible reason may be the definition of tumor extension (less
or more than 50% of total liver volume) which is somewhat subjective and may compromise the reliability
of CLIP in predicting patient outcomes [24-27] . Still, CLIP is recently ranked first for its ability to predict
[22]
survival .
GRETCH Score
GRoupe d’Etude et de Traitement du Carcinoma Hépatocellulaire (GRETCH) system was proposed by the
[8]
French group Goupe d’Etude et de in 1999 . This system was constructed with the analysis of 761 HCC
patients treated at 24 centers. The group has created a score quite similar to the CLIP aiming at a simple
classification that would predict survival. Unlike CLIP, GRETCH further includes performance status but
lacks tumor morphology information. GRETCH staging divides the patients into three risk groups (A, B,
C) on the basis of performance status, serum bilirubin, serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP), serum AFP and
portal vein obstruction on ultrasound [Table 4]. The overall survival (OS) differs markedly for the three
groups, with a one-year survival rate in group A (low risk to death) of 72%, compared to 34% in group B
(intermediate risk of death) and 7% in group C (high risk of death). The strength of this system is that it
is based on baseline characteristics that are routinely available at diagnosis and the scores allocated to the
respective predictive factors are based on the estimated Cox regression coefficient. However, in this study,
53% of HCC patients did not receive any specific therapy, while only 7.4% underwent surgical resection.
Therefore, this score may not be suitable for predicting the survival of HCC patients who undergo surgical
resection. In addition, this cohort mostly included patients at advanced stages. A recent comparison with
[15]
other staging systems has shown that it has limited prognostic capacity in patients with early HCC .