Page 237 - Read Online
P. 237
Shami-shah et al. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucleic Acids 2023;4:447-60 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/evcna.2023.14 Page 457
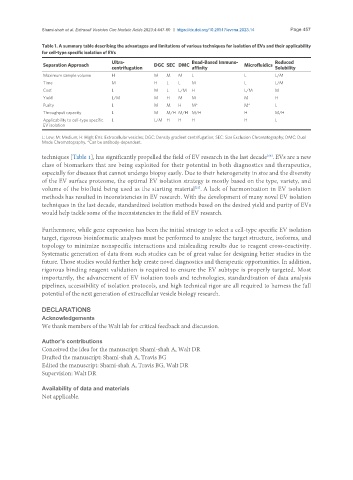
Table 1. A summary table describing the advantages and limitations of various techniques for isolation of EVs and their applicability
for cell-type specific isolation of EVs
Ultra- Bead-Based Immuno- Reduced
Separation Approach DGC SEC DMC Microfluidics
centrifugation affinity Solubility
Maximum sample volume H M M M L L L/M
Time M H L L M L L/M
Cost L M L L/M H L/M M
Yield L/M M H M M M H
Purity L M M H M* M* L
Throughput capacity L M M/H M/H M/H H M/H
Applicability to cell-type specific L L/M H H H H L
EV isolation
L: Low; M: Medium; H: High; EVs: Extracellular vesicles; DGC: Density gradient centrifugation; SEC: Size Exclusion Chromatography; DMC: Dual
Mode Chromatography. *Can be antibody-dependent.
techniques [Table 1], has significantly propelled the field of EV research in the last decade . EVs are a new
[66]
class of biomarkers that are being exploited for their potential in both diagnostics and therapeutics,
especially for diseases that cannot undergo biopsy easily. Due to their heterogeneity in size and the diversity
of the EV surface proteome, the optimal EV isolation strategy is mostly based on the type, variety, and
[21]
volume of the biofluid being used as the starting material . A lack of harmonization in EV isolation
methods has resulted in inconsistencies in EV research. With the development of many novel EV isolation
techniques in the last decade, standardized isolation methods based on the desired yield and purity of EVs
would help tackle some of the inconsistencies in the field of EV research.
Furthermore, while gene expression has been the initial strategy to select a cell-type specific EV isolation
target, rigorous bioinformatic analyses must be performed to analyze the target structure, isoforms, and
topology to minimize nonspecific interactions and misleading results due to reagent cross-reactivity.
Systematic generation of data from such studies can be of great value for designing better studies in the
future. Those studies would further help create novel diagnostics and therapeutic opportunities. In addition,
rigorous binding reagent validation is required to ensure the EV subtype is properly targeted. Most
importantly, the advancement of EV isolation tools and technologies, standardization of data analysis
pipelines, accessibility of isolation protocols, and high technical rigor are all required to harness the full
potential of the next generation of extracellular vesicle biology research.
DECLARATIONS
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the Walt lab for critical feedback and discussion.
Author’s contributions
Conceived the idea for the manuscript: Shami-shah A, Walt DR
Drafted the manuscript: Shami-shah A, Travis BG
Edited the manuscript: Shami-shah A, Travis BG, Walt DR
Supervision: Walt DR
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.