Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Zhuang et al. Energy Mater. 2025, 5, 500015 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2024.90 Page 7 of 14
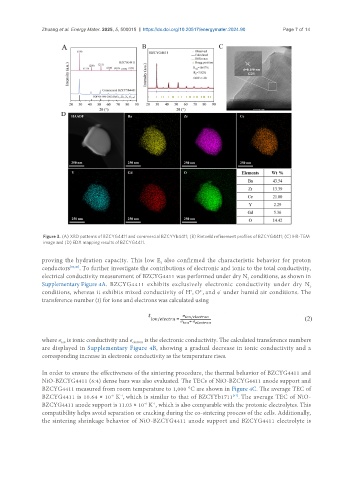
Figure 3. (A) XRD patterns of BZCYG4411 and commercial BZCYYb4411; (B) Rietveld refinement profiles of BZCYG4411; (C) HR-TEM
image and (D) EDX mapping results of BZCYG4411.
proving the hydration capacity. This low E also confirmed the characteristic behavior for proton
a
conductors [39,40] . To further investigate the contributions of electronic and ionic to the total conductivity,
electrical conductivity measurement of BZCYG4411 was performed under dry N conditions, as shown in
2
Supplementary Figure 4A. BZCYG4411 exhibits exclusively electronic conductivity under dry N
2
conditions, whereas it exhibits mixed conductivity of H , O , and e under humid air conditions. The
2-
+
-
transference number (t) for ions and electrons was calculated using
where σ is ionic conductivity and σ electron is the electronic conductivity. The calculated transference numbers
ion
are displayed in Supplementary Figure 4B, showing a gradual decrease in ionic conductivity and a
corresponding increase in electronic conductivity as the temperature rises.
In order to ensure the effectiveness of the sintering procedure, the thermal behavior of BZCYG4411 and
NiO-BZCYG4411 (6:4) dense bars was also evaluated. The TECs of NiO-BZCYG4411 anode support and
BZCYG4411 measured from room temperature to 1,000 °C are shown in Figure 4C. The average TEC of
BZCYG4411 is 10.64 × 10 K , which is similar to that of BZCYYb1711 . The average TEC of NiO-
[41]
-1
-6
BZCYG4411 anode support is 11.03 × 10 K , which is also comparable with the protonic electrolytes. This
-6
-1
compatibility helps avoid separation or cracking during the co-sintering process of the cells. Additionally,
the sintering shrinkage behavior of NiO-BZCYG4411 anode support and BZCYG4411 electrolyte is