Page 98 - Read Online
P. 98
Rehman et al. Energy Mater 2024;4:400068 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2024.06 Page 29 of 64
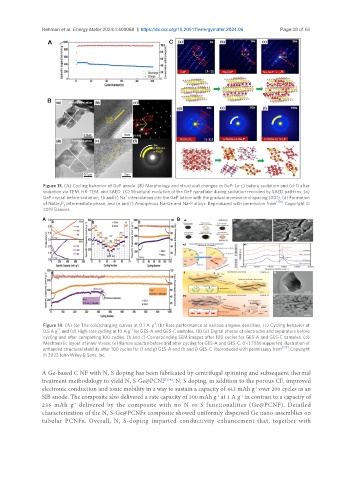
Figure 13. (A) Cycling behavior of GeP anode. (B) Morphology and structural changes in GeP: (a-c) before sodiation and (d-f) after
sodiation via TEM, HR-TEM, and SAED. (C) Structural evolution of the GeP nanoflake during sodiation recorded by SAED patterns. (a)
+
GeP crystal before sodiation, (b and c) Na intercalation into the GeP lattice with the gradual increase in d-spacing (001), (d) Formation
of NaGe P intermediate phase, and (e and f) Amorphous Na-Ge and Na-P alloys. Reproduced with permission from [170] . Copyright ©
3 3
2019 Elsevier.
-1
Figure 14. (A) (a) The (dis)charging curves at 0.1 A g , (b) Rate performance at various ampere densities, (c) Cycling behavior at
-1
-1
0.5 A g , and (d) High-rate cycling at 10 A g for GES-A and GES-C samples. (B) (a) Digital photos of electrodes and separators before
cycling and after completing 100 cycles. (b and c) Corresponding SEM images after 100 cycles for GES-A and GES-C samples. (d)
Mechanistic layout of inner stress. (e) Raman spectra before and after cycling for GES-A and GES-C. (f-i) TEM supported illustration of
enhanced structural stability after 100 cycles for (f and g) GES-A and (h and i) GES-C. Reproduced with permission from [173] . Copyright
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
A Ge-based C NF with N, S doping has been fabricated by centrifugal spinning and subsequent thermal
treatment methodology to yield N, S-Ge@PCNF . N, S doping, in addition to the porous CF, improved
[174]
electronic conduction and ionic mobility in a way to sustain a capacity of 443 mAh g over 200 cycles as an
-1
SIB anode. The composite also delivered a rate capacity of 300 mAh g at 1 A g in contrast to a capacity of
-1
-1
-1
236 mAh g delivered by the composite with no N or S functionalities (Ge@PCNF). Detailed
characterization of the N, S-Ge@PCNFs composite showed uniformly dispersed Ge nano-assemblies on
tubular PCNFs. Overall, N, S-doping imparted conductivity enhancement that, together with