Page 104 - Read Online
P. 104
Rehman et al. Energy Mater 2024;4:400068 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2024.06 Page 35 of 64
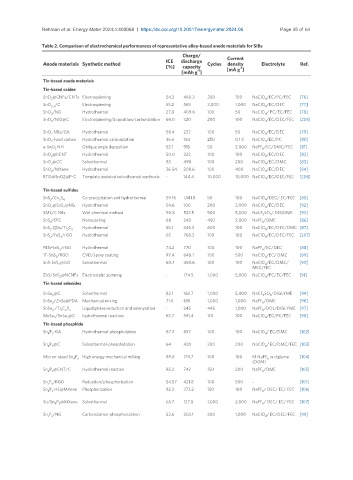
Table 2. Comparison of electrochemical performances of representative alloy-based anode materials for SIBs
Charge/ Current
Anode materials Synthetic method ICE discharge Cycles density Electrolyte Ref.
[%]
capacity
-1
-1
[mAh g ] [mA g ]
Tin-based anode materials
Tin-based oxides
SnO @CNFs/CNTs Electrospinning 54.3 460.3 200 100 NaClO /EC/PC/FEC [76]
2
4
SnO /C Electrospinning 55.2 565 2,000 1,000 NaClO /EC/DEC [77]
2-x 4
SnO /NG Hydrothermal 27.8 409.6 100 50 NaClO / PC/EC/FEC [78]
2
4
SnO /NiO@C Electrospinning/deposition/carbonization 69.0 320 200 100 NaClO /EC/DEC/FEC [205 ]
2 4
SnO NRs/GA Hydrothermal 58.4 232 100 50 NaClO /EC/DEC [79]
2
4
SnO -hard carbon Hydrothermal carbonization 36.6 184 250 0.1 C NaClO /EC/PC [80]
2 4
a-SnO NH Oblique angle deposition 53.1 915 50 2,000 NaPF /EC/DMC/FEC [81]
2
6
SnO @hCNT Hydrothermal 50.0 223 100 100 NaClO /EC/DEC [82]
2 4
SnO @CC Solvothermal 85 498 100 200 NaClO /EC/DMC [83]
4
2
SnO /MXene Hydrothermal 36.54 208.6 100 400 NaClO /EC/DEC [84]
2 4
BTO@SnO2@P-C Template assisted solvothermal synthesis - 144.4 10,000 10,000 NaClO /EC/DEC/FEC [206 ]
4
Tin-based sulfides
SnS /Co S Co-precipitation and hydrothermal 59.16 1,141.8 50 100 NaClO /DEC/ EC/FEC [85]
2 3 4 4
SnO @SnS @NG Hydrothermal 54.6 100 200 3,000 NaClO /EC/DEC [92]
2
2
4
SMS/C NBs Wet chemical method 90.8 522.5 500 5,000 NaCF SO / DEGDME [93]
3 3
SnS /EPC Nanocasting 68 340 450 2,000 NaPF /DME [86]
2
6
SnS QDs/Ti C Hydrothermal 55.1 345.3 600 100 NaClO /EC/DEC/DMC [87]
2 3 2 4
SnS /FeS /rGO Hydrothermal 65 768.3 100 100 NaClO /EC/DEC/FEC [207 ]
4
2
2
PEG-SnS /rGO Hydrothermal 74.2 770 100 100 NaPF /EC/DEC [88]
2 6
1T-SnS /RGO CVD/spray coating 97.4 648.1 100 500 NaClO /EC/ DMC [89]
4
2
SnS-SnS @GO Solvothermal 69.7 450.6 100 100 NaClO /EC/DMC/ [90]
2 4
MEC/FEC
ZnS/SnS @NCNFs Electrostatic spinning - 174.5 1,000 5,000 NaClO /PC/EC/FEC [91]
2 4
Tin-based selenides
SnSe @C Solvothermal 83.1 182.7 1,000 5,000 NaCF SO /DIGLYME [94]
2 3 3
SnSe /ZnSe@PDA Mechanical mixing 71.6 616 1,000 1,000 NaPF /DME [96]
6
2
SnSe /Ti C T Liquid phase reduction and selenylation - 245 445 1,000 NaPF /DOL/DIGLYME [97]
2 3 2 x 6
MoSe /SnSe @C hydrothermal reaction 63.7 591.4 110 100 NaClO /EC/PC/FEC [98]
4
2
2
Tin-based phosphide
Sn P -GA Hydrothermal-phosphidation 67.3 657 100 100 NaClO / EC/DMC [102 ]
4 3
4
Sn P @C Solvothermal-phosphidation 64 420 300 200 NaClO / EC/DMC/FEC [103 ]
4 3
4
Micron-sized Sn P High energy mechanical milling 89.8 719.7 100 100 M NaPF in diglyme [104]
4 3
6
(DGM)
Sn P @CNT/C Hydrothermal reaction 85.2 742 150 200 NaPF /DME [105]
4 3
6
Sn P /RGO Reduction/phosphorization 54.57 421.8 100 500 - [101]
x y
Sn P HS@MXene Phosphorization 82.3 373.2 150 100 NaPF / DEC/ EC/ FEC [106]
4 3
6
Sn/Sn P @MXene Solvothermal 65.7 127.8 1,000 2,000 NaPF / DEC/ EC/ FEC [107]
4 3
6
Sn P /NG Carbonization-phosphorization 52.6 203.1 300 1,000 NaClO / EC/DEC/FEC [99]
4
x y