Page 106 - Read Online
P. 106
Rehman et al. Energy Mater 2024;4:400068 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2024.06 Page 37 of 64
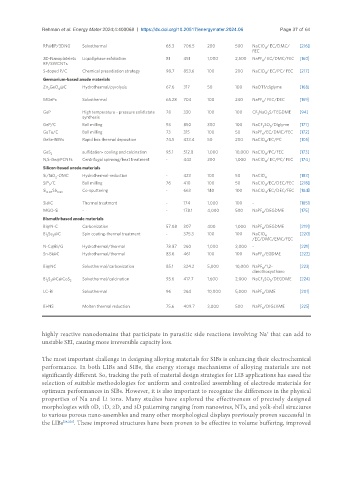
RP@BP/3DNG Solvothermal 65.3 706.5 200 500 NaClO / EC/DMC/ [216]
4
FEC
2D-Nanoplatelets Liquid phase exfoliation 81 451 1,000 2,500 NaPF / EC/DMC/FEC [160]
6
RP/SWCNTs
S-doped P/C Chemical presodiation strategy 98.7 853.6 100 200 NaClO / EC/PC/ FEC [217]
4
Germanium-based anode materials
Zn GeO @C Hydrothermal/pyrolysis 67.6 317 50 100 NaOTf/diglyme [168]
4
2
MGePx Solvothermal 65.28 704 100 240 NaPF / FEC/DEC [169 ]
6
GeP High temperature - pressure solid state 78 330 100 100 CF NaO S/TEGDME [94]
3 3
synthesis
GeP/C Ball milling 93 850 300 100 NaCF SO /Diglyme [171]
3 3
GeTe/C Ball milling 73 315 100 50 NaPF /EC/DMC/FEC [172]
6
GeSe-NWs Rapid box thermal deposition 74.5 433.4 50 200 NaClO /EC/PC [105]
4
GeS sulfidation- cooling and calcination 95.1 512.8 1,000 10,000 NaClO /PC/FEC [173]
2 4
N,S-Ge@PCNFs Centrifugal spinning/heat treatment - 443 200 1,000 NaClO / EC/PC/ FEC [174]
4
Silicon-based anode materials
Si/SiO -OMC Hydrothermal-reduction - 423 100 50 NaClO 4 [183]
2
SiP /C Ball milling 76 410 100 50 NaClO /EC/DEC/FEC [218]
2 4
Si 0.07 Sb 0.93 Co-sputtering - 663 140 100 NaClO /EC/DEC/FEC [184]
4
Si@C Thermal treatment - 174 1,000 100 - [185]
MGO-Si - - 178.1 4,000 500 NaPF /DEGDME [175]
6
Bismuth-based anode materials
Bi@N-C Carbonization 57.08 307 400 1,000 NaPF /DEGDME [219]
6
Bi Se @C Spin coating-thermal treatment - 375.3 100 100 NaClO 4 [220 ]
3
2
/EC/DMC/EMC/FEC
N-C@Bi/G Hydrothermal/thermal 78.87 260 1,000 2,000 - [221]
Sn-Bi@C Hydrothermal/thermal 83.6 461 100 100 NaPF /EGDME [222]
6
Bi@NC Solvothermal/carbonization 85.1 324.2 5,000 10,000 NaPF /1,2- [223 ]
6
dimethoxyethane
Bi S @C@CoS 2 Solvothermal/calcination 93.6 417.7 1,600 2,000 NaCF SO /DEGDME [224 ]
2 3
3
3
LC-Bi Solvothermal 96 264 10,000 5,000 NaPF /DME [201]
6
Bi-NS Molten thermal reduction 75.6 409.7 3,000 500 NaPF /DIGLYME [225 ]
6
+
highly reactive nanodomains that participate in parasitic side reactions involving Na that can add to
unstable SEI, causing more irreversible capacity loss.
The most important challenge in designing alloying materials for SIBs is enhancing their electrochemical
performance. In both LIBs and SIBs, the energy storage mechanisms of alloying materials are not
significantly different. So, tracking the path of material design strategies for LIB applications has eased the
selection of suitable methodologies for uniform and controlled assembling of electrode materials for
optimum performances in SIBs. However, it is also important to recognize the differences in the physical
properties of Na and Li ions. Many studies have explored the effectiveness of precisely designed
morphologies with 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D patterning ranging from nanowires, NTs, and yolk-shell structures
to various porous nano-assembles and many other morphological displays previously proven successful in
the LIBs [24,226] . These improved structures have been proven to be effective in volume buffering, improved