Page 192 - Read Online
P. 192
Page 8 of 12 Cui et al. Energy Mater 2023;3:300023 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2022.90
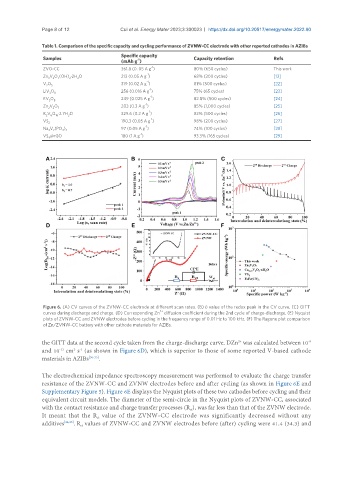
Table 1. Comparison of the specific capacity and cycling performance of ZVNW-CC electrode with other reported cathodes in AZIBs
Specific capacity
Samples -1 Capacity retention Refs
(mAh g )
-1
ZVO-CC 361.8 (0. 05 A g ) 80% (650 cycles) This work
-1
Zn V O (OH) ·2H O 213 (0.05 A g ) 68% (300 cycles) [13]
2
2
3
7
2
-1
V O 319 (0.02 A g ) 81% (500 cycles) [22]
2 5
-1
LiV O 8 256 (0.016 A g ) 75% (65 cycles) [23]
3
-1
KV O 249 (0.025 A g ) 82.8% (500 cycles) [24]
3 8
-1
Zn V O 7 203 (0.3 A g ) 85% (1,000 cycles) [25]
2
2
-1
K V O ·2.7H O 329.6 (0.2 A g ) 82% (500 cycles) [26]
2
6
2
16
-1
VS 2 190.3 (0.05 A g ) 98% (200 cycles) [27]
-1
Na V (PO ) 97 (0.05 A g ) 74% (100 cycles) [28]
4 3
2
3
-1
VS @rGO 180 (1 A g ) 93.3% (165 cycles) [29]
4
Figure 6. (A) CV curves of the ZVNW-CC electrode at different scan rates. (B) b value of the redox peak in the CV curve. (C) GITT
2+
curves during discharge and charge. (D) Corresponding Zn diffusion coefficient during the 2nd cycle of charge-discharge. (E) Nyquist
plots of ZVNW-CC and ZVNW electrodes before cycling in the frequency range of 0.01 Hz to 100 kHz. (F) The Ragone plot comparison
of Zn/ZVNW-CC battery with other cathode materials for AZIBs.
the GITT data at the second cycle taken from the charge-discharge curve. DZn was calculated between 10
-9
2+
2
and 10 cm s (as shown in Figure 6D), which is superior to those of some reported V-based cathode
-11
-1
materials in AZIBs [30-33] .
The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurement was performed to evaluate the charge transfer
resistance of the ZVNW-CC and ZVNW electrodes before and after cycling (as shown in Figure 6E and
Supplementary Figure 5). Figure 6E displays the Nyquist plots of these two cathodes before cycling and their
equivalent circuit models. The diameter of the semi-circle in the Nyquist plots of ZVNW-CC, associated
with the contact resistance and charge transfer processes (R ), was far less than that of the ZVNW electrode.
ct
It meant that the R value of the ZVNW-CC electrode was significantly decreased without any
ct
additives [34,35] . R values of ZVNW-CC and ZVNW electrodes before (after) cycling were 41.4 (34.3) and
ct