Page 16 - Read Online
P. 16
Zhang et al. Chem Synth 2023;3:10 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cs.2022.40 Page 9 of 35
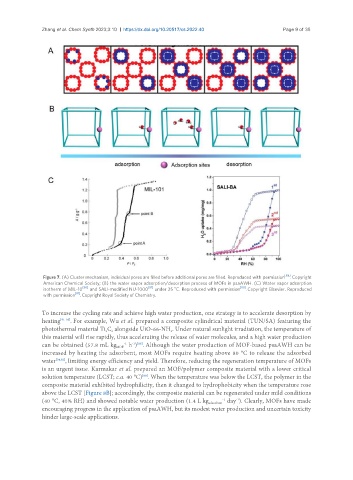
Figure 7. (A) Cluster mechanism, individual pores are filled before additional pores are filled. Reproduced with permission [68] . Copyright
American Chemical Society; (B) the water vapor adsorption/desorption process of MOFs in psaAWH. (C) Water vapor adsorption
o
isotherm of MIL-10 [80] and SALI-modified NU-1000 [81] under 25 C. Reproduced with permission [80] . Copyright Elsevier. Reproduced
with permission [81] . Copyright Royal Society of Chemistry.
To increase the cycling rate and achieve high water production, one strategy is to accelerate desorption by
heating [91-93] . For example, Wu et al. prepared a composite cylindrical material (TUN/SA) featuring the
photothermal material Ti C alongside UiO-66-NH . Under natural sunlight irradiation, the temperature of
2
2
3
this material will rise rapidly, thus accelerating the release of water molecules, and a high water production
can be obtained (57.8 mL kg MOF -1 h ) . Although the water production of MOF-based psaAWH can be
-1 [86]
increased by heating the adsorbent, most MOFs require heating above 80 °C to release the adsorbed
water [34,92] , limiting energy efficiency and yield. Therefore, reducing the regeneration temperature of MOFs
is an urgent issue. Karmakar et al. prepared an MOF/polymer composite material with a lower critical
solution temperature (LCST; c.a. 40 °C) . When the temperature was below the LCST, the polymer in the
[88]
composite material exhibited hydrophilicity, then it changed to hydrophobicity when the temperature rose
above the LCST [Figure 8B]; accordingly, the composite material can be regenerated under mild conditions
(40 °C, 40% RH) and showed notable water production (1.4 L kg adsorbent -1 day ). Clearly, MOFs have made
-1
encouraging progress in the application of psaAWH, but its modest water production and uncertain toxicity
hinder large-scale applications.