Page 59 - Read Online
P. 59
Li et al. Chem Synth 2023;3:30 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cs.2023.16 Page 11 of 17
th
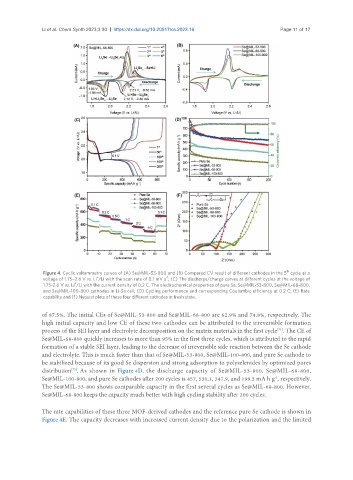
Figure 4. Cyclic voltammetry curves of (A) Se@MIL-53-800 and (B) Compared CV result of different cathodes in the 5 cycle at a
-1
+
voltage of 1.75–2.6 V vs. Li /Li with the scan rate of 0.1 mV s ; (C) The discharge/charge curves at different cycles at the voltage of
+
1.75-2.6 V vs. Li /Li with the current density of 0.2 C. The electrochemical properties of pure Se, Se@MIL-53-800, Se@MIL-68-800,
and Se@MIL-100-800 cathodes in Li-Se cell; (D) Cycling performance and corresponding Coulombic efficiency at 0.2 C; (E) Rate
capability and (F) Nyquist plots of these four different cathodes at fresh state.
of 87.5%. The initial CEs of Se@MIL-53-800 and Se@MIL-68-800 are 62.9% and 74.8%, respectively. The
high initial capacity and low CE of these two cathodes can be attributed to the irreversible formation
[71]
process of the SEI layer and electrolyte decomposition on the matrix materials in the first cycle . The CE of
Se@MIL-68-800 quickly increases to more than 95% in the first three cycles, which is attributed to the rapid
formation of a stable SEI layer, leading to the decrease of irreversible side reaction between the Se cathode
and electrolyte. This is much faster than that of Se@MIL-53-800, Se@MIL-100-800, and pure Se cathode to
be stabilized because of its good Se dispersion and strong adsorption to polyselenides by optimized pores
distribution . As shown in Figure 4D, the discharge capacity of Se@MIL-53-800, Se@MIL-68-800,
[72]
Se@MIL-100-800, and pure Se cathodes after 200 cycles is 457, 530.1, 347.9, and 199.3 mA h g , respectively.
-1
The Se@MIL-53-800 shows comparable capacity in the first several cycles as Se@MIL-68-800. However,
Se@MIL-68-800 keeps the capacity much better with high cycling stability after 200 cycles.
The rate capabilities of these three MOF-derived cathodes and the reference pure Se cathode is shown in
Figure 4E. The capacity decreases with increased current density due to the polarization and the limited