Page 37 - Read Online
P. 37
Chen et al. Complex Eng Syst 2023;3:8 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ces.2022.50 Page 3 of 15
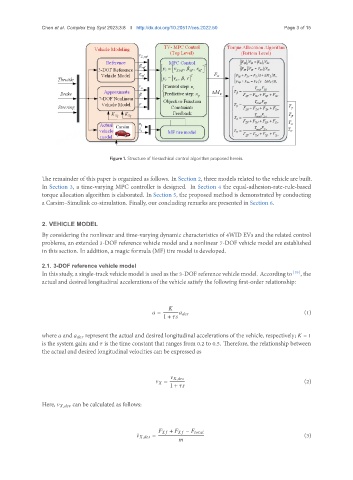
Figure 1. Structure of hierarchical control algorithm proposed herein.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, three models related to the vehicle are built.
In Section 3, a time-varying MPC controller is designed. In Section 4 the equal-adhesion-rate-rule-based
torque allocation algorithm is elaborated. In Section 5, the proposed method is demonstrated by conducting
a Carsim–Simulink co-simulation. Finally, our concluding remarks are presented in Section 6.
2. VEHICLE MODEL
By considering the nonlinear and time-varying dynamic characteristics of 4WID EVs and the related control
problems, an extended 3-DOF reference vehicle model and a nonlinear 7-DOF vehicle model are established
in this section. In addition, a magic formula (MF) tire model is developed.
2.1. 3-DOF reference vehicle model
In this study, a single-track vehicle model is used as the 3-DOF reference vehicle model. According to [19] , the
actual and desired longitudinal accelerations of the vehicle satisfy the following first-order relationship:
= (1)
1 +
where and represent the actual and desired longitudinal accelerations of the vehicle, respectively; = 1
is the system gain; and is the time constant that ranges from 0.2 to 0.5. Therefore, the relationship between
the actual and desired longitudinal velocities can be expressed as
,
= (2)
1 +
Here, , can be calculated as follows:
+ −
¤ , = (3)