Page 34 - Read Online
P. 34
Lee et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2020;3:980-91 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2020.73 Page 985
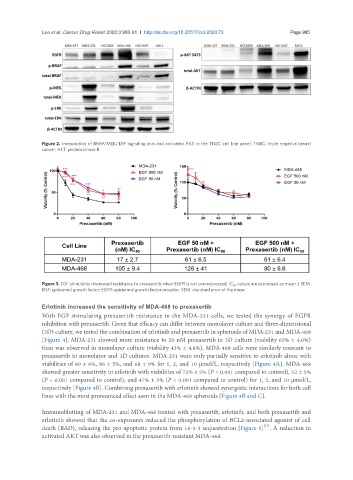
Figure 2. Immunoblot of BRAF/MEK/ERF signaling axis and activated AKT in the TNBC cell line panel. TNBC: triple negative breast
cancer; AKT: protein kinase B
Figure 3. EGF stimulation increased resistance to prexasertib when EGFR is not overexpressed. IC 50 values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
EGF: epidermal growth factor; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; SEM: standard error of the mean
Erlotinib increased the sensitivity of MDA-468 to prexasertib
With EGF stimulating prexasertib resistance in the MDA-231 cells, we tested the synergy of EGFR
inhibition with prexasertib. Given that efficacy can differ between monolayer culture and three-dimensional
(3D) culture, we tested the combination of erlotinib and prexasertib in spheroids of MDA-231 and MDA-468
[Figure 4]. MDA-231 showed more resistance to 20 nM prexasertib in 3D culture (viability 63% ± 4.0%)
than was observed in monolayer culture (viability 43% ± 4.8%). MDA-468 cells were similarly resistant to
prexasertib in monolayer and 3D cultures. MDA-231 were only partially sensitive to erlotinib alone with
viabilities of 89 ± 6%, 86 ± 5%, and 68 ± 9% for 1, 2, and 10 µmol/L, respectively [Figure 4A]. MDA-468
showed greater sensitivity to erlotinib with viabilities of 72% ± 5% (P < 0.001 compared to control), 52 ± 5%
(P < 0.001 compared to control), and 47% ± 5% (P < 0.001 compared to control) for 1, 2, and 10 µmol/L,
respectively [Figure 4B]. Combining prexasertib with erlotinib showed synergistic interactions for both cell
lines with the most pronounced effect seen in the MDA-468 spheroids [Figure 4B and C].
Immunoblotting of MDA-231 and MDA-468 treated with prexasertib, erlotinib, and both prexasertib and
erlotinib showed that the co-exposures reduced the phosphorylation of BCL2-associated agonist of cell
[24]
death (BAD), releasing the pro-apoptotic protein from 14-3-3 sequestration [Figure 5] . A reduction in
activated AKT was also observed in the prexasertib-resistant MDA-468.