Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
Sale et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:365-80 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.14 Page 375
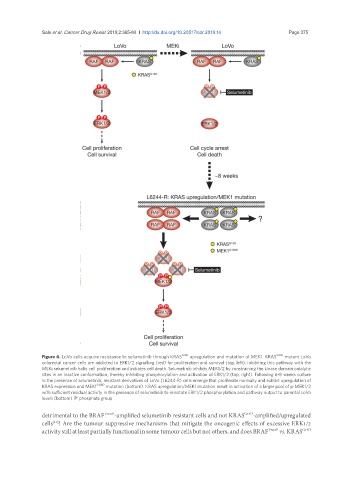
Figure 6. LoVo cells acquire resistance to selumetinib through KRAS G13D upregulation and mutation of MEK1. KRAS G13D -mutant LoVo
colorectal cancer cells are addicted to ERK1/2 signalling (red) for proliferation and survival (top, left); inhibiting this pathway with the
MEKi selumetinib halts cell proliferation and initiates cell death. Selumetinib inhibits MEK1/2 by constraining the kinase domain catalytic
sites in an inactive conformation, thereby inhibiting phosphorylation and activation of ERK1/2 (top, right). Following 6-8 weeks culture
in the presence of selumetinib, resistant derivatives of LoVo (L6244-R) cells emerge that proliferate normally and exhibit upregulation of
KRAS expression and MEK1 G128D mutation (bottom). KRAS upregulation/MEK1 mutation result in activation of a larger pool of p-MEK1/2
with sufficient residual activity in the presence of selumetinib to reinstate ERK1/2 phosphorylation and pathway output to parental LoVo
levels (bottom). P: phosphate group
detrimental to the BRAF V600E -amplified selumetinib resistant cells and not KRAS G13D -amplified/upregulated
cells ? Are the tumour suppressive mechanisms that mitigate the oncogenic effects of excessive ERK1/2
[11]
activity still at least partially functional in some tumour cells but not others, and does BRAF V600E vs. KRAS G13D