Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Page 374 Sale et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:365-80 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.14
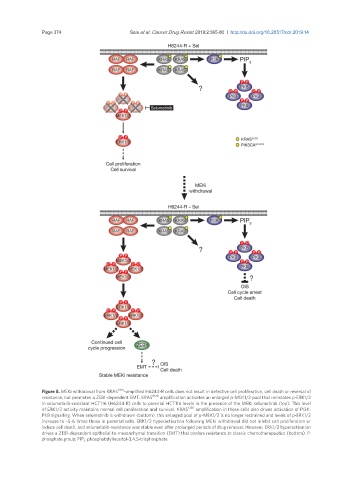
Figure 5. MEKi withdrawal from KRAS G13D -amplified H6244-R cells does not result in defective cell proliferation, cell death or reversal of
resistance, but promotes a ZEB1-dependent EMT. KRAS G13D amplification activates an enlarged p-MEK1/2 pool that reinstates p-ERK1/2
in selumetinib-resistant HCT116 (H6244-R) cells to parental HCT116 levels in the presence of the MEKi selumetinib (top). This level
of ERK1/2 activity maintains normal cell proliferation and survival. KRAS G13D amplification in these cells also drives activation of PI3K-
PKB signalling. When selumetinib is withdrawn (bottom), this enlarged pool of p-MEK1/2 is no longer restrained and levels of p-ERK1/2
increase to ~5-6 times those in parental cells. ERK1/2 hyperactivation following MEKi withdrawal did not inhibit cell proliferation or
induce cell death, and selumetinib-resistance was stable even after prolonged periods of drug removal. However, ERK1/2 hyperactivation
drives a ZEB1-dependent epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) that confers resistance to classic chemotherapeutics (bottom). P:
phosphate group; PIP 3 : phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate