Page 20 - Read Online
P. 20
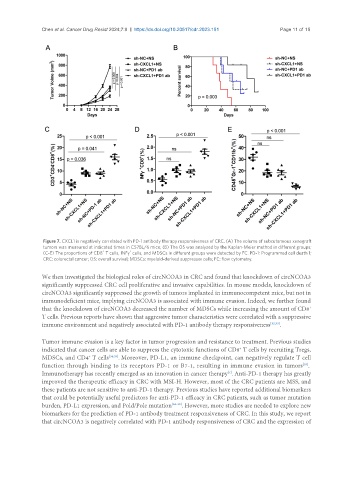
Chen et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2024;7:9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2023.151 Page 11 of 15
Figure 7. CXCL1 is negatively correlated with PD-1 antibody therapy responsiveness of CRC. (A) The volume of subcutaneous xenograft
tumors was measured at indicated times in C57BL/6 mice; (B) The OS was analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier method in different groups;
+
+
(C-E) The proportions of CD8 T cells, INFγ cells, and MDSCs in different groups were detected by FC. PD-1: Programmed cell death 1;
CRC: colorectal cancer; OS: overall survival; MDSCs: myeloid-derived suppressor cells; FC: flow cytometry.
We then investigated the biological roles of circNCOA3 in CRC and found that knockdown of circNCOA3
significantly suppressed CRC cell proliferative and invasive capabilities. In mouse models, knockdown of
circNCOA3 significantly suppressed the growth of tumors implanted in immunocompetent mice, but not in
immunodeficient mice, implying circNCOA3 is associated with immune evasion. Indeed, we further found
that the knockdown of circNCOA3 decreased the number of MDSCs while increasing the amount of CD8
+
T cells. Previous reports have shown that aggressive tumor characteristics were correlated with a suppressive
immune environment and negatively associated with PD-1 antibody therapy responsiveness [32,33] .
Tumor immune evasion is a key factor in tumor progression and resistance to treatment. Previous studies
+
indicated that cancer cells are able to suppress the cytotoxic functions of CD8 T cells by recruiting Tregs,
MDSCs, and CD4 T cells [34,35] . Moreover, PD-L1, an immune checkpoint, can negatively regulate T cell
+
[35]
function through binding to its receptors PD-1 or B7-1, resulting in immune evasion in tumors .
Immunotherapy has recently emerged as an innovation in cancer therapy . Anti-PD-1 therapy has greatly
[7]
improved the therapeutic efficacy in CRC with MSI-H. However, most of the CRC patients are MSS, and
these patients are not sensitive to anti-PD-1 therapy. Previous studies have reported additional biomarkers
that could be potentially useful predictors for anti-PD-1 efficacy in CRC patients, such as tumor mutation
burden, PD-L1 expression, and Pold/Pole mutation [36-38] . However, more studies are needed to explore new
biomarkers for the prediction of PD-1 antibody treatment responsiveness of CRC. In this study, we report
that circNCOA3 is negatively correlated with PD-1 antibody responsiveness of CRC and the expression of