Page 18 - Read Online
P. 18
Chen et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2024;7:9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2023.151 Page 9 of 15
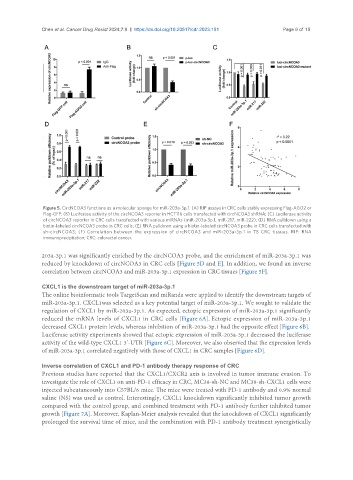
Figure 5. CircNCOA3 functions as a molecular sponge for miR-203a-3p.1. (A) RIP assays in CRC cells stably expressing Flag-AGO2 or
Flag-GFP; (B) Luciferase activity of the circNCOA3 reporter in HCT116 cells transfected with circNCOA3 shRNA; (C) Luciferase activity
of circNCOA3 reporter in CRC cells transfected with various miRNAs (miR-203a-3p.1, miR-217, miR-222); (D) RNA pulldown using a
biotin-labeled circNCOA3 probe in CRC cells; (E) RNA pulldown using a biotin-labeled circNCOA3 probe in CRC cells transfected with
sh-circNCOA3; (F) Correlation between the expression of circNCOA3 and miR-203a-3p.1 in 78 CRC tissues. RIP: RNA
immunoprecipitation; CRC: colorectal cancer.
203a-3p.1 was significantly enriched by the circNCOA3 probe, and the enrichment of miR-203a-3p.1 was
reduced by knockdown of circNCOA3 in CRC cells [Figure 5D and E]. In addition, we found an inverse
correlation between circNCOA3 and miR-203a-3p.1 expression in CRC tissues [Figure 5F].
CXCL1 is the downstream target of miR-203a-3p.1
The online bioinformatic tools TargetScan and miRanda were applied to identify the downstream targets of
miR-203a-3p.1. CXCL1was selected as a key potential target of miR-203a-3p.1. We sought to validate the
regulation of CXCL1 by miR-203a-3p.1. As expected, ectopic expression of miR-203a-3p.1 significantly
reduced the mRNA levels of CXCL1 in CRC cells [Figure 6A]. Ectopic expression of miR-203a-3p.1
decreased CXCL1 protein levels, whereas inhibition of miR-203a-3p.1 had the opposite effect [Figure 6B].
Luciferase activity experiments showed that ectopic expression of miR-203a-3p.1 decreased the luciferase
activity of the wild-type CXCL1 3’-UTR [Figure 6C]. Moreover, we also observed that the expression levels
of miR-203a-3p.1 correlated negatively with those of CXCL1 in CRC samples [Figure 6D].
Inverse correlation of CXCL1 and PD-1 antibody therapy response of CRC
Previous studies have reported that the CXCL1/CXCR2 axis is involved in tumor immune evasion. To
investigate the role of CXCL1 on anti-PD-1 efficacy in CRC, MC38-sh-NC and MC38-sh-CXCL1 cells were
injected subcutaneously into C57BL/6 mice. The mice were treated with PD-1 antibody and 0.9% normal
saline (NS) was used as control. Interestingly, CXCL1 knockdown significantly inhibited tumor growth
compared with the control group, and combined treatment with PD-1 antibody further inhibited tumor
growth [Figure 7A]. Moreover, Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that the knockdown of CXCL1 significantly
prolonged the survival time of mice, and the combination with PD-1 antibody treatment synergistically