Page 19 - Read Online
P. 19
Page 10 of 15 Chen et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2024;7:9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2023.151
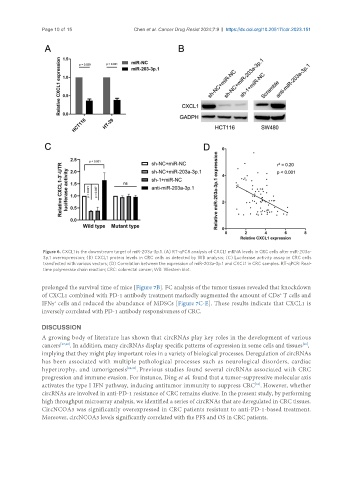
Figure 6. CXCL1 is the downstream target of miR-203a-3p.1. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of CXCL1 mRNA levels in CRC cells after miR-203a-
3p.1 overexpression; (B) CXCL1 protein levels in CRC cells as detected by WB analysis; (C) Luciferase activity assay in CRC cells
transfected with various vectors; (D) Correlation between the expression of miR-203a-3p.1 and CXCL1 in CRC samples. RT-qPCR: Real-
time polymerase chain reaction; CRC: colorectal cancer; WB: Western blot.
prolonged the survival time of mice [Figure 7B]. FC analysis of the tumor tissues revealed that knockdown
of CXCL1 combined with PD-1 antibody treatment markedly augmented the amount of CD8 T cells and
+
+
IFNγ cells and reduced the abundance of MDSCs [Figure 7C-E]. These results indicate that CXCL1 is
inversely correlated with PD-1 antibody responsiveness of CRC.
DISCUSSION
A growing body of literature has shown that circRNAs play key roles in the development of various
cancers [27,28] . In addition, many circRNAs display specific patterns of expression in some cells and tissues ,
[29]
implying that they might play important roles in a variety of biological processes. Deregulation of circRNAs
has been associated with multiple pathological processes such as neurological disorders, cardiac
hypertrophy, and tumorigenesis [28,30] . Previous studies found several circRNAs associated with CRC
progression and immune evasion. For instance, Ding et al. found that a tumor-suppressive molecular axis
activates the type I IFN pathway, inducing antitumor immunity to suppress CRC . However, whether
[31]
circRNAs are involved in anti-PD-1 resistance of CRC remains elusive. In the present study, by performing
high throughput microarray analysis, we identified a series of circRNAs that are deregulated in CRC tissues.
CircNCOA3 was significantly overexpressed in CRC patients resistant to anti-PD-1-based treatment.
Moreover, circNCOA3 levels significantly correlated with the PFS and OS in CRC patients.