Page 99 - Read Online
P. 99
Page 57 Xu et al. Art Int Surg 2023;3:48-63 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2022.33
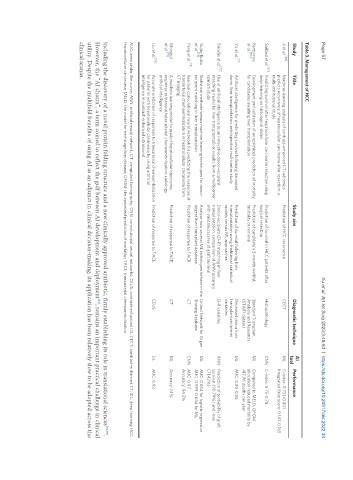
Table 3. Management of HCC
AI
Study Title Study aim Diagnostic technique Performance
tool
[66]
Ji et al. Machine-learning analysis of contrast-enhanced CT radiomics Prediction of HCC recurrence CECT ML C-index: 0.733-0.801
predicts recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection: a Integrated Brier score: 0.147-0.165
multi-institutional study
Saillard et al. [67] Predicting survival after hepatocellular carcinoma resection using Prediction of survival in HCC patients after Histopathology CNN C-index: 0.75-0.78
deep learning on histological slides surgical resection
Bertsimas Development and validation of an optimized prediction of mortality Prediction of candidate's 3-month waitlist Standard Transplant ML Compared to MELD, OPOM
[70]
et al. for candidates awaiting liver transplantation mortality or removal Analysis and Research allocation reduced mortality by
(STAR) dataset 417.96 deaths per year
Yu et al. [71] Artificial intelligence for predicting survival following deceased Prediction of survival following liver Deceased donor liver ML AUC: 0.80-0.85
donor liver transplantation: retrospective multicenter study transplantation using traditional statistical transplant recipients
models versus ML approaches variables
[72]
Briceño et al. Use of artificial intelligence as an innovative donor-recipient Donor-recipient (D-R) matching in liver D-R variables ANN Prediction of probability of graft
matching model for liver transplantation: results from a multicenter transplantation, comparison of ANN accuracy survival (90.79%) and -loss
spanish study with validated scores of graft survival (71.42%)
Gujio-Rubio Statistical methods versus machine learning techniques for donor- Analyze how several ML techniques behave in the United Network for Organ ML AUC: 0.654 for logistic regression
[73]
et al. recipient matching in liver transplantation largest liver transplant database Sharing database AUC: 0.599-0.644 for ML
[74]
Peng et al. Residual convolutional neural network for predicting the response of Prediction of response to TACE CT CNN AUC: 0.97
transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma from Accuracy: 84.3%
CT imaging
Morshid A machine learning model to predict hepatocellular carcinoma Prediction of response to TACE CT ML Accuracy: 74%
et al. [75] response to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. radiology
artificial intelligence
[76]
Liu et al. Accurate prediction of responses to transarterial chemoembolization Prediction of response to TACE CEUS DL AUC: 0.93
for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma by using artificial
intelligence in contrast-enhanced ultrasound
AUC: area under the curve; ANN: artificial neural network; CT: computed tomography; CNN: convolutional neural networks; CEUS: contrast-enhanced US; CECT: contrast-enhanced CT; DL: deep learning HCC:
Hepatocellular carcinoma; MELD: the model for end-stage liver disease; OPOM: the optimized prediction of mortality; TACE: transarterial chemoembolization.
including the discovery of a novel protein folding structure and a new clinically approved antibiotic, firmly establishing its role in translational sciences [78,79] .
[80]
However, the “AI chasm”, a term coined to reflect the gulf between AI development and deployment , remains an important practical challenge in clinical
utility. Despite the multifold benefits of using AI as an adjunct in clinical decision-making, its application has been relatively slow to be adopted across the
clinical arenas.