Page 80 - Read Online
P. 80
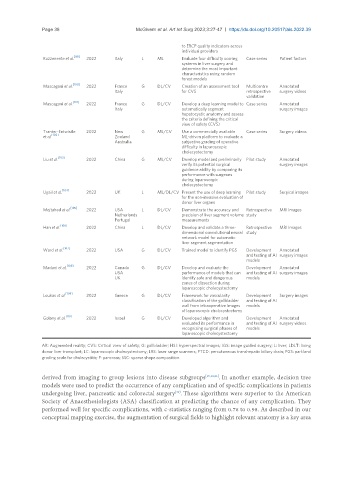
Page 38 McGivern et al. Art Int Surg 2023;3:27-47 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2022.39
to ERCP quality indicators across
individual providers
[99]
Ruzzenente et al. 2022 Italy L ML Evaluate four difficulty scoring Case series Patient factors
systems in liver surgery and
determine the most important
characteristics using random
forest models
Mascagani et al. [100] 2022 France G DL/CV Creation of an assessment tool Multicentre Annotated
Italy for CVS retrospective surgery videos
validation
[101]
Mascagani et al. 2022 France G DL/CV Develop a deep learning model to Case series Annotated
Italy automatically segment surgery images
hepatocystic anatomy and assess
the criteria defining the critical
view of safety (CVS)
Tranter-Entwistle 2022 New G ML/CV Use a commercially available Case series Surgery videos
[102]
et al. Zealand ML-driven platform to evaluate a
Australia subjective grading of operative
difficulty in laparoscopic
cholecystectomy
Liu et al. [103] 2022 China G ML/CV Develop model and preliminarily Pilot study Annotated
verify its potential surgical surgery images
guidance ability by comparing its
performance with surgeons
during laparoscopic
cholecystectomy
[104]
Ugail et al. 2022 UK L ML/DL/CV Present the use of deep learning Pilot study Surgical images
for the non-invasive evaluation of
donor liver organs
Mojtahed et al. [105] 2022 USA L DL/CV Demonstrate the accuracy and Retrospective MRI images
Netherlands precision of liver segment volume study
Portugal measurements
[106]
Han et al. 2022 China L DL/CV Develop and validate a three- Retrospective MRI images
dimensional convolutional neural study
network model for automatic
liver segment segmentation
[107]
Ward et al. 2022 USA G DL/CV Trained model to identify PGS Development Annotated
and testing of AI surgery images
models
[108]
Madani et al. 2022 Canada G DL/CV Develop and evaluate the Development Annotated
USA performance of models that can and testing of AI surgery images
UK identify safe and dangerous models
zones of dissection during
laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Loukas et al. [109] 2022 Greece G DL/CV Framework for vascularity Development Surgery images
classification of the gallbladder and testing of AI
wall from intraoperative images models
of laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Golany et al. [110] 2022 Israel G DL/CV Developed algorithm and Development Annotated
evaluated its performance in and testing of AI surgery videos
recognizing surgical phases of models
laparoscopic cholecystectomy
AR: Augmented reality; CVS: Critical view of safety; G: gallbladder; HSI: hyperspectral images; IGS: image guided surgery; L: liver; LDLT: living
donor liver transplant; LC: laparoscopic cholecystectomy; LRS: laser range scanners; PTCD: percutaneous transhepatic biliary drain; PGS: parkland
grading scale for cholecystitis; P: pancreas; SSC: sparse shape composition.
derived from imaging to group lesions into disease subgroups [15,18,21] . In another example, decision tree
models were used to predict the occurrence of any complication and of specific complications in patients
[49]
undergoing liver, pancreatic and colorectal surgery . These algorithms were superior to the American
Society of Anaesthesiologists (ASA) classification at predicting the chance of any complication. They
performed well for specific complications, with c-statistics ranging from 0.76 to 0.98. As described in our
conceptual mapping exercise, the augmentation of surgical fields to highlight relevant anatomy is a key area