Page 21 - Read Online
P. 21
Skoreński et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2023;2:6 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2022.21 Page 17 of 23
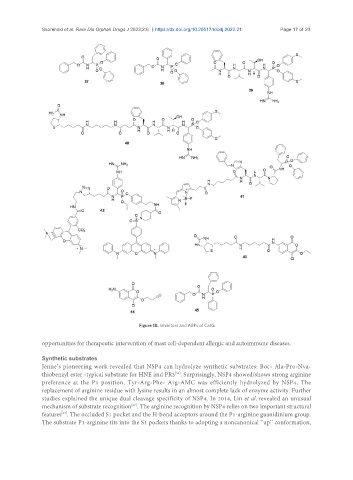
Figure 18. Inhibitors and ABPs of CatG.
opportunities for therapeutic intervention of mast cell-dependent allergic and autoimmune diseases.
Synthetic substrates
Jenne’s pioneering work revealed that NSP4 can hydrolyze synthetic substrates: Boc- Ala-Pro-Nva-
[84]
thiobenzyl ester -typical substrate for HNE and PR3 . Surprisingly, NSP4 showed/shows strong arginine
preference at the P1 position. Tyr-Arg-Phe- Arg-AMC was efficiently hydrolyzed by NSP4. The
replacement of arginine residue with lysine results in an almost complete lack of enzyme activity. Further
studies explained the unique dual cleavage specificity of NSP4. In 2014, Lin et al. revealed an unusual
mechanism of substrate recognition . The arginine recognition by NSP4 relies on two important structural
[87]
features . The occluded S1 pocket and the H-bond acceptors around the P1-arginine guanidinium group.
[87]
The substrate P1-arginine tits into the S1 pockets thanks to adopting a noncanonical ‘‘up’’ conformation,