Page 18 - Read Online
P. 18
Page 14 of 23 Skoreński et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2023;2:6 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2022.21
[67]
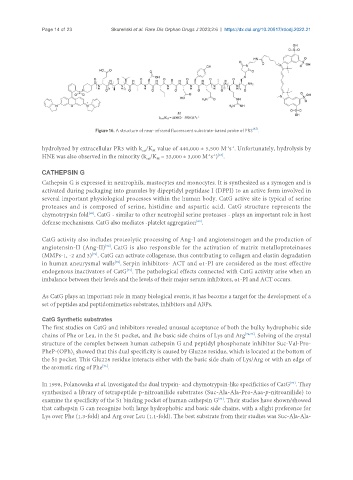
Figure 16. A structure of near-infrared fluorescent substrate-based probe of PR3 .
hydrolyzed by extracellular PR3 with k /K value of 440,000 ± 5,500 M s . Unfortunately, hydrolysis by
-1 -1
cat
M
-1 -1 [67]
HNE was also observed in the minority (k /K = 33,000 ± 3,000 M s ) .
M
cat
CATHEPSIN G
Cathepsin G is expressed in neutrophils, mastocytes and monocytes. It is synthesized as a zymogen and is
activated during packaging into granules by dipeptidyl peptidase I (DPPI) to an active form involved in
several important physiological processes within the human body. CatG active site is typical of serine
proteases and is composed of serine, histidine and aspartic acid. CatG structure represents the
chymotrypsin fold . CatG - similar to other neutrophil serine proteases - plays an important role in host
[68]
defense mechanisms. CatG also mediates -platelet aggregation .
[69]
CatG activity also includes proteolytic processing of Ang-I and angiotensinogen and the production of
angiotensin-II (Ang-II) . CatG is also responsible for the activation of matrix metalloproteinases
[70]
(MMPs-1, -2 and 3) . CatG can activate collagenase, thus contributing to collagen and elastin degradation
[71]
in human aneurysmal walls . Serpin inhibitors- ACT and α1-PI are considered as the most effective
[72]
endogenous inactivators of CatG . The pathological effects connected with CatG activity arise when an
[73]
imbalance between their levels and the levels of their major serum inhibitors, α1-PI and ACT occurs.
As CatG plays an important role in many biological events, it has become a target for the development of a
set of peptides and peptidomimetics substrates, inhibitors and ABPs.
CatG Synthetic substrates
The first studies on CatG and inhibitors revealed unusual acceptance of both the bulky hydrophobic side
chains of Phe or Leu, in the S1 pocket, and the basic side chains of Lys and Arg [74,75] . Solving of the crystal
structure of the complex between human cathepsin G and peptidyl phosphonate inhibitor Suc-Val-Pro-
PheP-(OPh) showed that this dual specificity is caused by Glu226 residue, which is located at the bottom of
2
the S1 pocket. This Glu226 residue interacts either with the basic side chain of Lys/Arg or with an edge of
the aromatic ring of Phe .
[76]
In 1998, Polanowska et al. investigated the dual trypsin- and chymotrypsin-like specificities of CatG . They
[74]
synthesized a library of tetrapeptide p-nitroanilide substrates (Suc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Aaa-p-nitroanilide) to
examine the specificity of the S1 binding pocket of human cathepsin G . Their studies have shown/showed
[74]
that cathepsin G can recognize both large hydrophobic and basic side chains, with a slight preference for
Lys over Phe (1.3-fold) and Arg over Leu (1.1-fold). The best substrate from their studies was Suc-Ala-Ala-