Page 19 - Read Online
P. 19
Liu et al. Microstructures 2023;3:2023001 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/microstructures.2022.23 Page 15 of 21
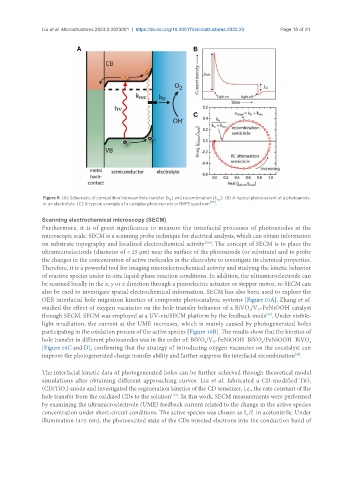
Figure 9. (A) Schematic of competition between hole transfer (k ) and recombination (k ). (B) A typical photocurrent of a photoanode
tr rec
[98]
in an electrolyte. (C) A typical example of a complex photocurrent or IMPS spectrum .
Scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM)
Furthermore, it is of great significance to measure the interfacial processes of photoanodes at the
microscopic scale. SECM is a scanning probe technique for electrical analysis, which can obtain information
on substrate topography and localized electrochemical activity . The concept of SECM is to place the
[100]
ultramicroelectrode (diameter of < 25 μm) near the surface of the photoanode (or substrate) and to probe
the changes in the concentration of active molecules in the electrolyte to investigate its chemical properties.
Therefore, it is a powerful tool for imaging microelectrochemical activity and studying the kinetic behavior
of reactive species under in-situ liquid-phase reaction conditions. In addition, the ultramicroelectrode can
be scanned locally in the x, y or z direction through a piezoelectric actuator or stepper motor, so SECM can
also be used to investigate spatial electrochemical information. SECM has also been used to explore the
OER interfacial hole migration kinetics of composite photocatalytic systems [Figure 10A]. Zhang et al.
studied the effect of oxygen vacancies on the hole transfer behavior of a BiVO /V -FeNiOOH catalyst
O
4
through SECM. SECM was employed at a UV-vis/SECM platform by the feedback mode . Under visible-
[38]
light irradiation, the current at the UME increases, which is mainly caused by photogenerated holes
participating in the oxidation process of the active species [Figure 10B]. The results show that the kinetics of
hole transfer in different photoanodes was in the order of: BiVO /V -FeNiOOH BiVO /FeNiOOH BiVO
4
4
O
4
[Figure 10C and D], confirming that the strategy of introducing oxygen vacancies on the cocatalyst can
[38]
improve the photogenerated charge transfer ability and further suppress the interfacial recombination .
The interfacial kinetic data of photogenerated holes can be further achieved through theoretical model
simulations after obtaining different approaching curves. Liu et al. fabricated a CD-modified TiO
2
(CD/TiO ) anode and investigated the regeneration kinetics of the CD sensitizer, i.e., the rate constant of the
2
[101]
hole transfer from the oxidized CDs to the solution . In this work, SECM measurements were performed
by examining the ultramicroelectrode (UME) feedback current related to the change in the active species
concentration under short-circuit conditions. The active species was chosen as I /I in acetonitrile. Under
-
-
3
illumination (475 nm), the photoexcited state of the CDs injected electrons into the conduction band of