Page 129 - Read Online
P. 129
Page 10 of 21 Carr et al. Vessel Plus 2020;4:12 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2020.01
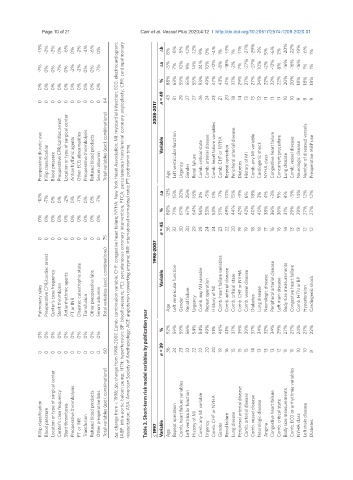
-13% -2% -2% 0% -6% 0% -2% -4% -6% 0% Δb 8% -8% -5% -12% -12% 9% 0% -4% 1% -13% 1% -11% -27% -29% -2% 5% -6% 2% -20% -22% -19% -6% 1%
-7% 0% 0% -7% 0% -2% -2% 0% 0% -7% Δa -5% 7% 10% 9% 14% 24% 10% -12% -8% -18% -2% 7% -27% -27% 10% -2% -12% 8% -16% -16% -16% 1% 1%
% 88% 63% 59% 55% 55% 53% 49% 47% 43% 41% 37% 29% 27% 27% 24% 22% 22% 22% 20% 20% 18% 18% 18%
0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 64 2008-2017 n = 49 43 31 29 27 27 26 24 23 21 20 18 14 13 13 12 11 11 11 10 10 9 9 9
Preoperative diuretic use Killip classification Blood pressure Preoperative CPR/cardiac arrest Location or type of surgical center Antiarrhythmic agents Other ECG abnormalities Preoperative thrombolysis Refused blood products Serum albumin Total variables (excl. combinations) Variable Age Left ventricular function Urgency Gender Renal failure Comb. critical state Comb. arterial disease Comb. heart failure variables Comb. CHF or NYHA Repeat
-10% -7% 0% 0% -2% 0% -7% 0% 0% -7% Δa -12% 15% 20% 25% 16% 2% -5% 0% -7% 10% 15% -9% 6% 18% 3% 4% -3% 9% 4% -5% 14% 12% 12%
% 80% 71% 67% 67% 64% 56% 53% 53% 51% 49% 44% 42% 42% 40% 40% 38% 36% 36% 31% 29% 29% 27% 27%
0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
n = 45 36 32 30 30 29 25 24 24 23 22 20 19 19 18 18 17 16 16 14 13 13 12 12
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 75 Δa: change from < 1998; Δb: change from 1998-2007. Comb: combination variable; CHF: congestive heart failure; NYHA: New York Heart Association; MI: myocardial infarction; ECG: electrocardiogram; IABP: intra-aortic baloon pump; HTN: hypertension; BP: blood pressure; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; PTCA: percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty; CPR: cardiopulmonary 1998-2007
Pulmonary rales Preoperative CPR/cardiac arrest Center’s case frequency Stent thrombosis Antiarrhythmic agents PT or INR Disaster, catastrophic state Transfusion Other preoperative labs Serum albumin Total variables (excl. combinations) resuscitation; ASA: American Society of Anethesiology; ACE: angiotensin converting enzyme; INR: international normalized ratio; PT: prothromin time Variable Age Left ventricular function Gender Renal failure Ur
% 92% 59% 59% 56% 54% 54% 49% 51% 46% 41% 37% 39% 39% 37% 34% 32% 34% 29% 27% 27% 24% 27% 22%
0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
n = 39 36 24 23 22 22 22 20 20 19 16 15 15 15 14 12 10 10
60
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Table 3. Short-term risk model variables by publication year 13 13 13 11 11 8
Killip classification Blood pressure Location or type of surgical center Center’s case frequency Stent thrombosis Preoperative thrombolysis PT or INR Transfusion Refused blood products Other preoperative labs Total variables (excl. combinations) ≤ 1997 Variable Age Repeat operation Comb. heart failure variables Left ventricular function History of MI Comb. any MI variable Urgency Comb. CHF or NYHA Gender Renal failure Lung disease Perip