Page 392 - Read Online
P. 392
Page 6 of 13 Iqbal et al. Vessel Plus 2019;3:40 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.28
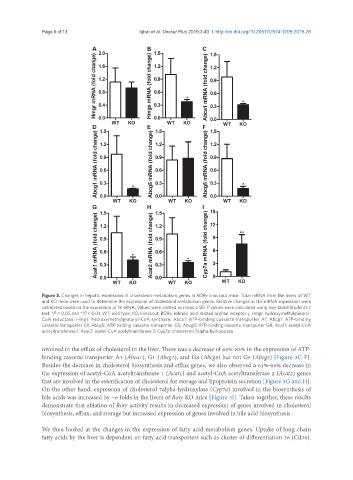
Figure 3. Changes in hepatic expression of cholesterol metabolism genes in RORγ knockout mice. Total mRNA from the livers of WT
and KO mice were used to determine the expression of cholesterol metabolism genes. Relative changes in the mRNA expression were
calculated based on the expression of 18 sRNA. Values were plotted as mean ± SD. P values were calculated using two-tailed Student’s t
test. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. WT: wild type; KO: knockout; RORγ: retinoic acid-related orphan receptor γ; Hmgr: hydroxymethylglutaryl-
CoA reductase; Hmgs: hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase; Abca1: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; Abcg1: ATP-binding
cassette transporter G1; Abcg5: ATP-binding cassette transporter G5; Abcg8: ATP-binding cassette transporter G8; Acat1: acetyl-CoA
acetyltransferase 1; Acat2: acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 2; Cyp7a: cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase
involved in the efflux of cholesterol in the liver. There was a decrease of 65%-83% in the expression of ATP-
binding cassette transporter A1 (Abca1), G1 (Abcg1), and G8 (Abcg8) but not G5 (Abcg5) [Figure 3C-F].
Besides the decrease in cholesterol biosynthesis and efflux genes, we also observed a 61%-65% decrease in
the expression of acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 1 (Acat1) and acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 2 (Acat2) genes
that are involved in the esterification of cholesterol for storage and lipoprotein secretion [Figure 3G and H].
On the other hand, expression of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (Cyp7a) involved in the biosynthesis of
bile acids was increased by ~6 folds in the livers of Rorγ KO mice [Figure 3I]. Taken together, these results
demonstrate that ablation of Rorγ activity results in decreased expression of genes involved in cholesterol
biosynthesis, efflux, and storage but increased expression of genes involved in bile acid biosynthesis.
We then looked at the changes in the expression of fatty acid metabolism genes. Uptake of long-chain
fatty acids by the liver is dependent on fatty acid transporters such as cluster of differentiation 36 (Cd36).