Page 349 - Read Online
P. 349
Page 12 of 13 Kumar et al. Vessel Plus 2019;3:35 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.006
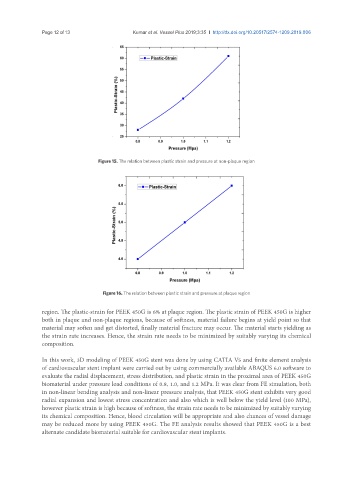
Figure 15. The relation between plastic strain and pressure at non-plaque region
Figure 16. The relation between plastic strain and pressure at plaque region
region. The plastic-strain for PEEK 450G is 6% at plaque region. The plastic strain of PEEK 450G is higher
both in plaque and non-plaque regions, because of softness, material failure begins at yield point so that
material may soften and get distorted, finally material fracture may occur. The material starts yielding as
the strain rate increases. Hence, the strain rate needs to be minimized by suitably varying its chemical
composition.
In this work, 3D modeling of PEEK 450G stent was done by using CATIA V5 and finite element analysis
of cardiovascular stent implant were carried out by using commercially available ABAQUS 6.0 software to
evaluate the radial displacement, stress distribution, and plastic strain in the proximal area of PEEK 450G
biomaterial under pressure load conditions of 0.8, 1.0, and 1.2 MPa. It was clear from FE simulation, both
in non-linear bending analysis and non-linear pressure analysis, that PEEK 450G stent exhibits very good
radial expansion and lowest stress concentration and also which is well below the yield level (100 MPa),
however plastic strain is high because of softness, the strain rate needs to be minimized by suitably varying
its chemical composition. Hence, blood circulation will be appropriate and also chances of vessel damage
may be reduced more by using PEEK 450G. The FE analysis results showed that PEEK 450G is a best
alternate candidate biomaterial suitable for cardiovascular stent implants.