Page 354 - Read Online
P. 354
Page 4 of 8 Radhakrishnan et al. Vessel Plus 2019;3:36 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.23
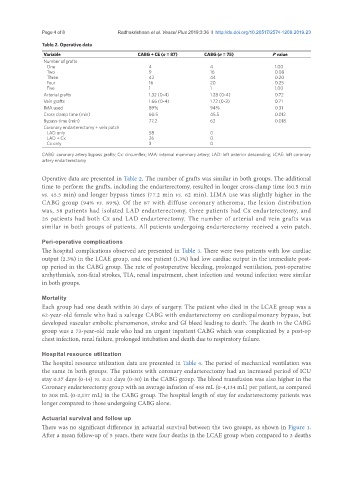
Table 2. Operative data
Variable CABG + CE (n = 87) CABG (n = 75) P value
Number of grafts
One 4 4 1.00
Two 9 16 0.08
Three 42 44 0.20
Four 16 20 0.25
Five 1 1 1.00
Arterial grafts 1.32 (0-4) 1.28 (0-4) 0.72
Vein grafts 1.66 (0-4) 1.72 (0-3) 0.71
IMA used 89% 94% 0.31
Cross clamp time (min) 60.5 45.5 0.012
Bypass time (min) 77.2 62 0.018
Coronary endarterectomy + vein patch
LAD only 58 0
LAD + Cx 26 0
Cx only 3 0
CABG: coronary artery bypass grafts; Cx: circumflex; IMA: internal mammary artery; LAD: left anterior descending; LCAE: left coronary
artery endarterectomy
Operative data are presented in Table 2. The number of grafts was similar in both groups. The additional
time to perform the grafts, including the endarterectomy, resulted in longer cross-clamp time (60.5 min
vs. 45.5 min) and longer bypass times (77.2 min vs. 62 min). LIMA use was slightly higher in the
CABG group (94% vs. 89%). Of the 87 with diffuse coronary atheroma, the lesion distribution
was, 58 patients had isolated LAD endarterectomy, three patients had Cx endarterectomy, and
26 patients had both Cx and LAD endarterectomy. The number of arterial and vein grafts was
similar in both groups of patients. All patients undergoing endarterectomy received a vein patch.
Peri-operative complications
The hospital complications observed are presented in Table 3. There were two patients with low cardiac
output (2.3%) in the LCAE group, and one patient (1.3%) had low cardiac output in the immediate post-
op period in the CABG group. The rate of postoperative bleeding, prolonged ventilation, post-operative
arrhythmia’s, non-fatal strokes, TIA, renal impairment, chest infection and wound infection were similar
in both groups.
Mortality
Each group had one death within 30 days of surgery. The patient who died in the LCAE group was a
62-year-old female who had a salvage CABG with endarterectomy on cardiopulmonary bypass, but
developed vascular embolic phenomenon, stroke and GI bleed leading to death. The death in the CABG
group was a 73-year-old male who had an urgent inpatient CABG which was complicated by a post-op
chest infection, renal failure, prolonged intubation and death due to respiratory failure.
Hospital resource utilization
The hospital resource utilization data are presented in Table 4. The period of mechanical ventilation was
the same in both groups. The patients with coronary endarterectomy had an increased period of ICU
stay 0.37 days (0-14) vs. 0.13 days (0-30) in the CABG group. The blood transfusion was also higher in the
Coronary endarterectomy group with an average infusion of 458 mL (0-4,134 mL) per patient, as compared
to 308 mL (0-2,137 mL) in the CABG group. The hospital length of stay for endarterectomy patients was
longer compared to those undergoing CABG alone.
Actuarial survival and follow up
There was no significant difference in actuarial survival between the two groups, as shown in Figure 1.
After a mean follow-up of 5 years, there were four deaths in the LCAE group when compared to 3 deaths